Table of Contents
Introduction:
Zirconia dental prosthesis sintering involves the high-temperature sintering of zirconia ceramic materials used in dental restorations. This process densifies the zirconia particles, forming a hard, durable, and biocompatible dental prosthesis.
It is widely used to manufacture crowns, bridges, inlays, and other dental restorations, ensuring excellent mechanical properties and aesthetics.
Precautions for Using Zirconia Sintering Furnace:
1. Crowns or long bridges after staining must be dried under an infrared drying lamp at a baking temperature below 100°C for 30-90 minutes depending on the number of prostheses, to fully remove moisture from the surface and inside the prostheses. Otherwise, uneven staining, uneven shrinkage, cracking, and contamination of the furnace chamber may occur.
2. During drying and sintering, the occlusal surface of the prostheses must face down.
3. Replace zirconia beads and crucibles in time after repeated use to avoid affecting sintering results.
4. It is recommended to tighten the screws connecting the heating rods and conductive braids every six months to prevent loosening due to thermal expansion and contraction, which could lead to poor connections and breakage of the heating rods.
5. Clean the sintering furnace every three months, scraping off impurities inside the furnace chamber. After cleaning, perform an empty sintering cycle with waste zirconia blocks.
6. It is recommended to open the furnace door at temperatures below 80°C to remove the prostheses to avoid thermal shock. Otherwise, the prostheses may develop microcracks.
Two Key Indicators Determining Zirconia Sintering Results:
1. Temperature inside the furnace chamber.
2. Purity inside the furnace chamber.
Common Sintering Defects and Solutions:
Uneven or Inaccurate Temperature:
Issue: Zirconia appears white, has poor translucency, bridge ends warp, or crowns crack.
Solution: Ensure uniformity and accuracy of the sintering furnace temperature, and use high-quality temperature control equipment.
Impurities Inside the Furnace Chamber (Impurities in Furnace Lining; Impurities on Heating Rods):
Issue: Zirconia appears yellow or red, with white or black spots on the surface.
Solution: Use high-purity furnace linings and heating rods, and clean the furnace chamber regularly.
Zirconia Dental Prosthesis Sintering Process:
Preparation of Zirconia Powder:
Mix high-purity zirconia powder with stabilizers (such as yttrium, lanthanum, etc.) to ensure the stability of zirconia at high temperatures.
Forming:
Mix the zirconia powder with an appropriate amount of binder. Use pressing, injection molding, or mold forming methods to compress the mixture into the initial shape of the tooth, forming a green body.
Debinding:
Perform debinding treatment on the formed zirconia green body to remove the organic binder and other volatile substances introduced during forming. The debinding process is usually carried out at a lower temperature to avoid cracking during sudden heating.
Presintering:
Presinter the green body at a lower temperature (800°C-1000°C) to initially bond the zirconia particles, increasing the strength of the green body for subsequent processing.
Machining:
Perform necessary mechanical processing on the presintered zirconia green body, such as trimming, grinding, and polishing, to obtain the required precise shape and size.
High-Temperature Sintering:
Perform final sintering on the machined zirconia green body at high temperatures. The sintering temperature is generally between 1350°C and 1550°C, with the sintering time depending on specific process requirements. The sintering process causes zirconia particles to bond together, forming a dense solid structure, thereby improving its mechanical strength and durability.
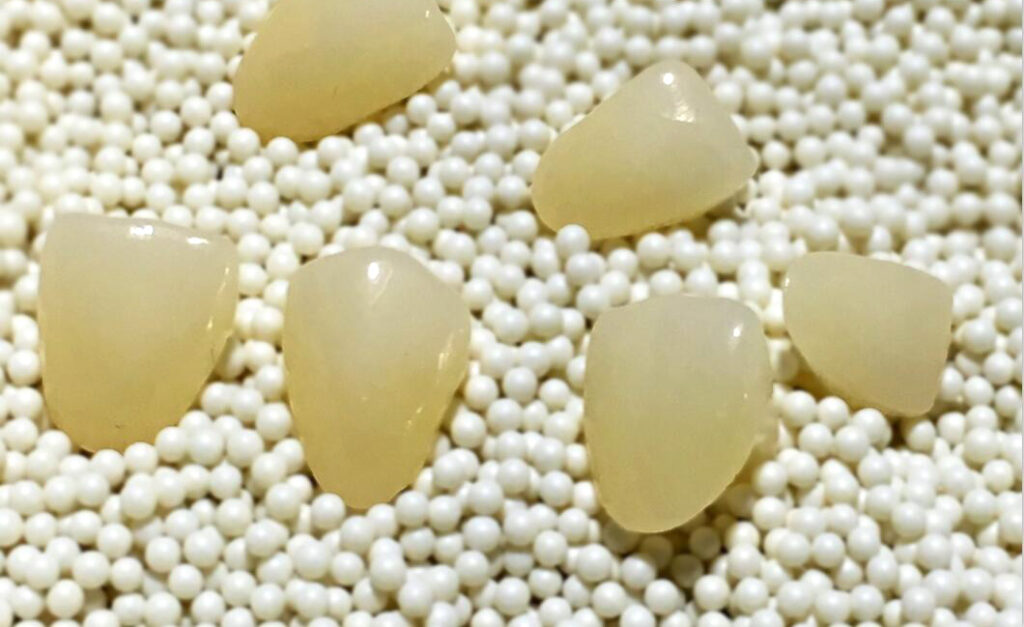

Post-Processing:
Further post-processing may be required for the sintered zirconia dental prosthesis, such as fine grinding, polishing, and coloring, to meet clinical aesthetic and functional requirements.
Quality Inspection:
Conduct strict quality inspections on the sintered zirconia dental prosthesis, checking its dimensions, shape, surface finish, and mechanical properties to ensure it meets standards and clinical requirements.
Solutions for Greenish-Yellow, Non-Translucent, and Under-Sintered Zirconia Dental Prostheses:
The zirconia dental prosthesis sintering furnace uses molybdenum disilicide rods as heating elements. Due to different compositions of zirconia blocks and colorants from various manufacturers, multiple accumulations of volatiles from zirconia blocks at high temperatures may damage and peel off the protective layer (SiO2) of the heating elements, leading to discoloration and non-translucent sintering of the prostheses.
To address this issue, bake the prostheses in an oven at over 170°C for 30-60 minutes before sintering to fully eliminate volatiles, and then proceed with high-temperature sintering.
After multiple sintering cycles, if the insulating zirconia beads appear yellow, observe the heating elements for peeling. If peeling is slight, replace the zirconia beads and perform an empty sintering cycle (1600°C) with the heating equipment.
If peeling is severe, replace the heating elements. After replacing the new heating elements, perform an empty sintering cycle (1600°C) to ensure a complete protective layer on the heating element surface before proceeding with prosthesis sintering.
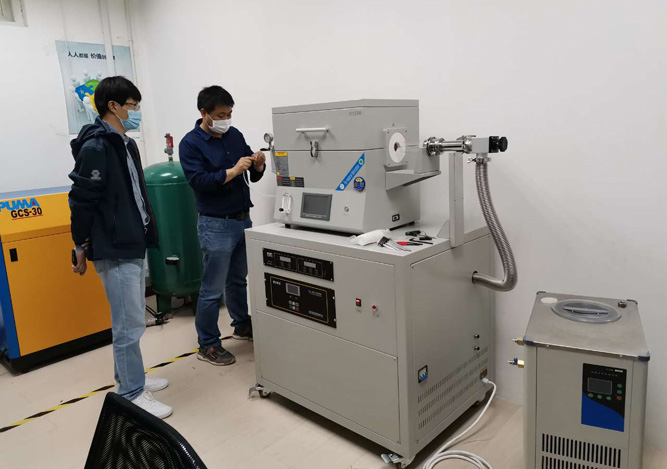
ZYLAB Recommended Dental Prosthesis Sintering Furnace:
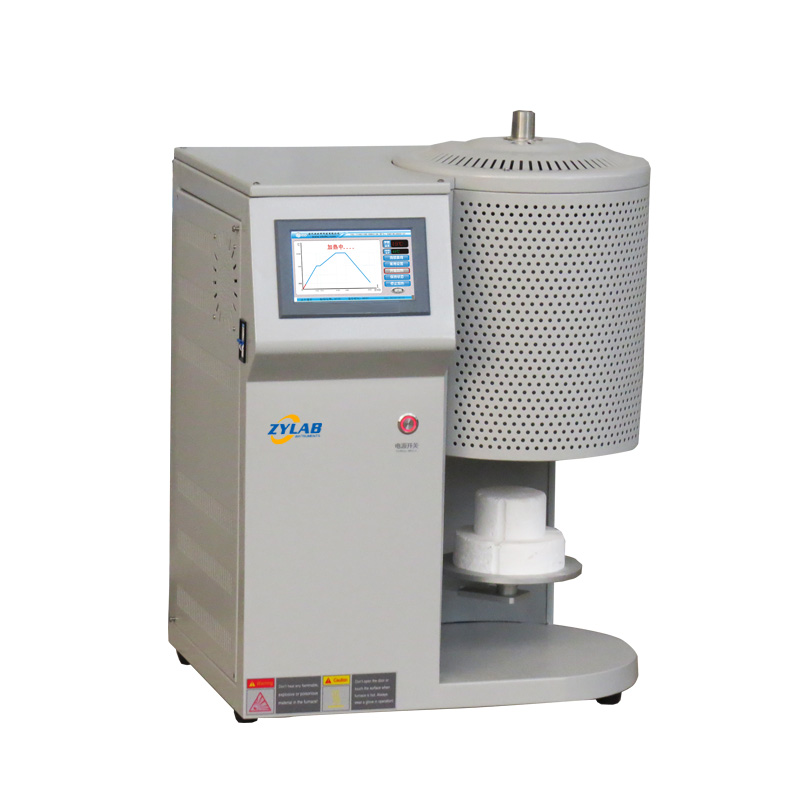
Dental Ceramic Furnace
1、Touchscreen control system.
2、Special high-density silicon carbide heating elements.
3、Electric lifting table.
4、Desktop design.
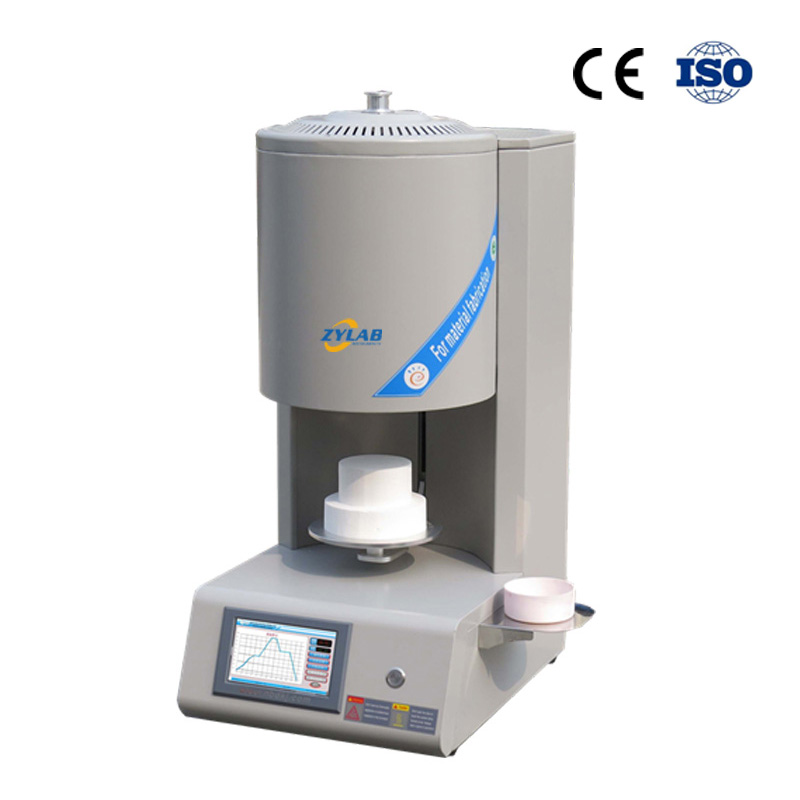
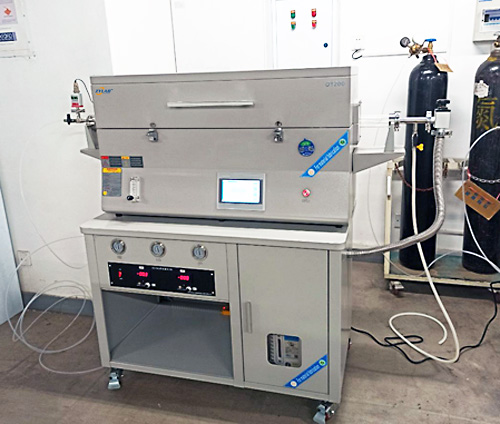
Professional 1700.C Zirconia Sintering Furnace
1、Come with vent design.
2、Ceramic fibre furnace chamber.
3、Electric lift table design.
4、Intelligent color touch screen temperature controller.
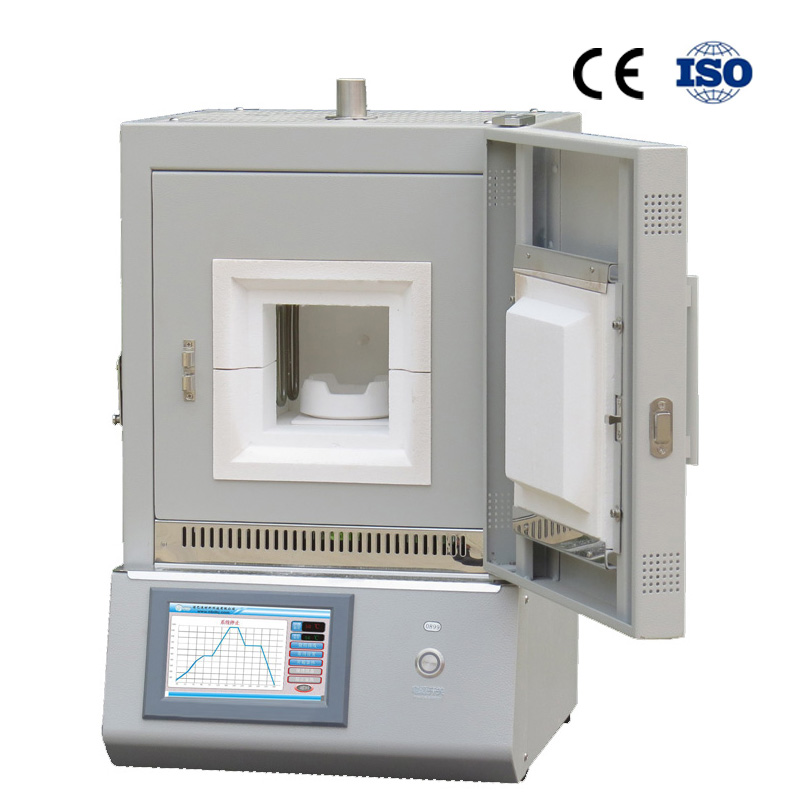
High Quality Dental Sintering Furnace
1、Come with vent hole.
2、Vacuum formed ceramic fiber furnace chamber.
3、Top quality furnace lining and high purity MoSi2 heating element.
4、Double layers steel casing with fan cooling.
5、Intelligent touch screen controller.







