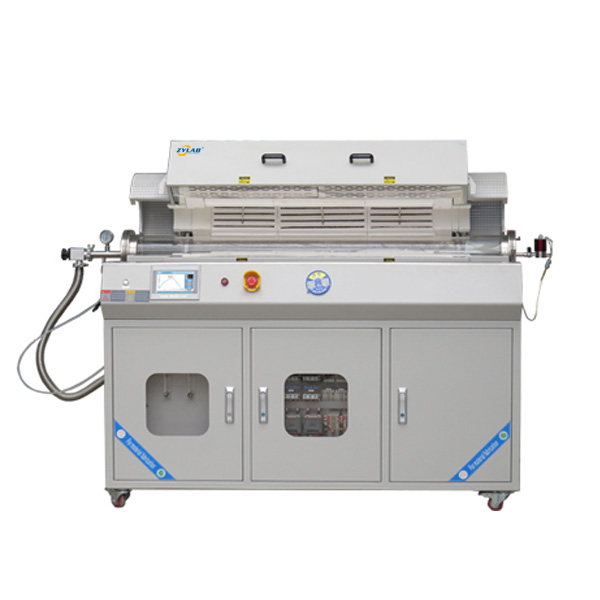
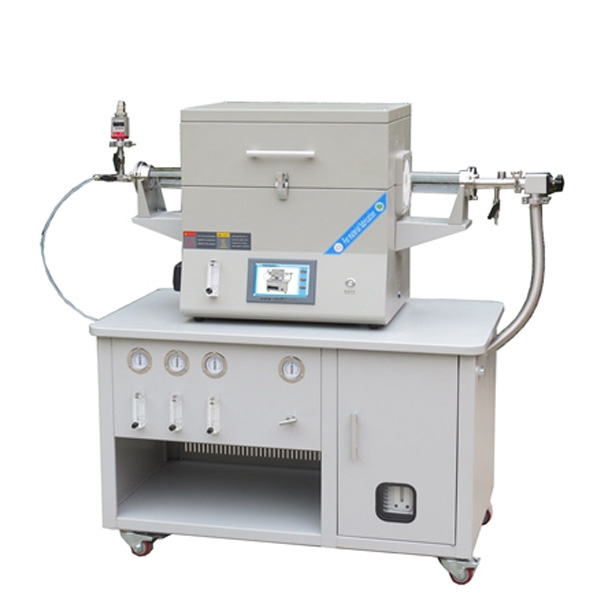
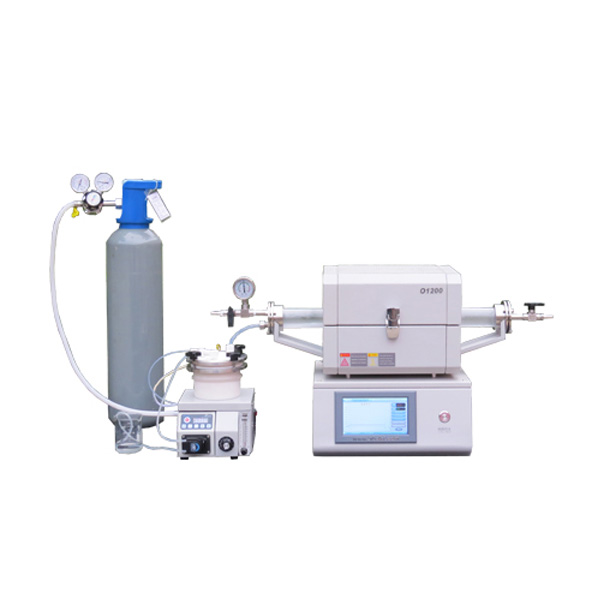
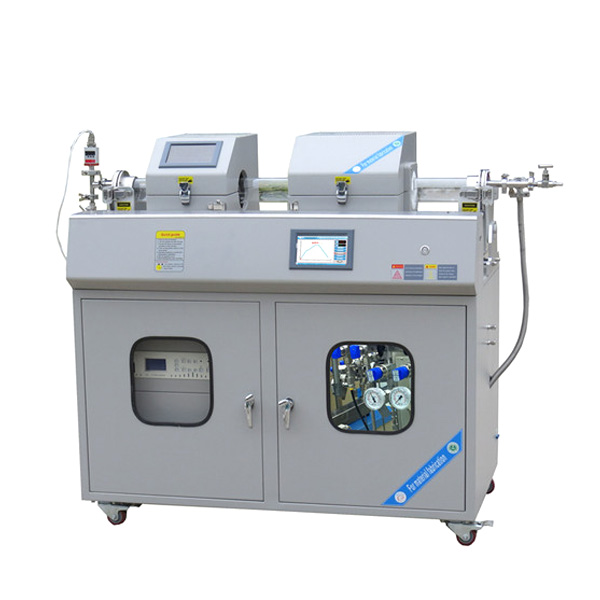
CVD Furnace System
A CVD furnace (Chemical Vapor Deposition furnace) is a specialized high-temperature system designed to deposit thin films or coatings onto substrates through chemical vapor deposition. In this process, gaseous precursors undergo chemical reactions or decomposition under controlled conditions, forming a solid thin film on the surface of the substrate.
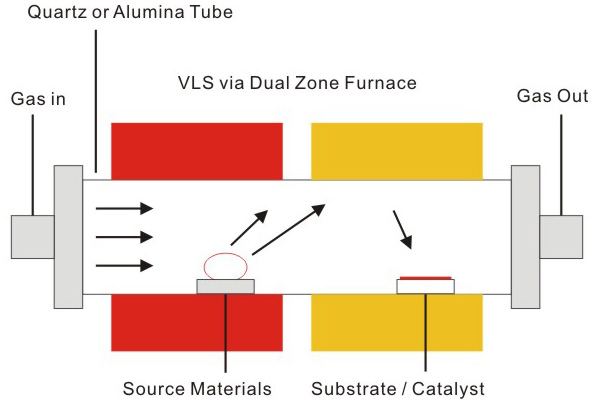
CVD furnaces are widely used in industries such as semiconductors, aerospace, optics, and material science for creating high-quality coatings or films.
Key Features of a CVD Furnace
- High Temperature Capability: Operates at temperatures typically ranging from 200°C to over 1500°C, depending on the specific application and materials being deposited.
- Gas Flow Control: Equipped with precise gas delivery systems to introduce precursor gases, carrier gases, and other reactive or inert gases.
- Atmosphere Control: Maintains specific environmental conditions such as vacuum, atmospheric pressure, or low-pressure environments (LPCVD).
- Uniform Heating: Designed for even heat distribution to ensure uniform thin-film deposition across the substrate, even on complex geometries.
- Exhaust System: Removes by-products and unreacted gases efficiently to maintain a clean deposition environment.
Working Principle
- Gas Introduction: Precursor gases are introduced into the furnace chamber through a gas flow system.
- Chemical Reaction: High temperatures in the furnace cause the precursor gases to react or decompose near the substrate surface.
- Thin Film Formation: The desired material deposits on the substrate surface as a solid film while by-products are carried away.
- Gas Removal: By-products and unused gases are evacuated through an exhaust or vacuum system.
Applications
- Semiconductors: Depositing films like silicon dioxide, silicon nitride, or polysilicon for integrated circuits.
- Solar Cells: Coating photovoltaic materials such as thin-film silicon or cadmium telluride.
- Optics: Applying anti-reflective or protective coatings on lenses and mirrors.
- Aerospace: Depositing wear-resistant or thermal barrier coatings.
- Nanotechnology: Growing nanomaterials like carbon nanotubes or graphene.
Types of CVD Furnaces
- Atmospheric Pressure CVD (APCVD): Operates at normal atmospheric pressure for faster deposition rates.
- Low-Pressure CVD (LPCVD): Utilizes reduced pressure to enhance uniformity and reduce contamination.
- Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD): Uses plasma to enable deposition at lower temperatures.
- Metal-Organic CVD (MOCVD): Employs metal-organic precursors for specific material deposition, commonly used in LEDs and optoelectronics.
CVD Furnace Images
CVD furnaces are essential tools for advanced material manufacturing, offering precise control over film thickness, uniformity, and material properties.
For more information or technical support, feel free to contact ZYLAB.
ZYLAB offers free quotes for all CVD furnaces and customized solutions!