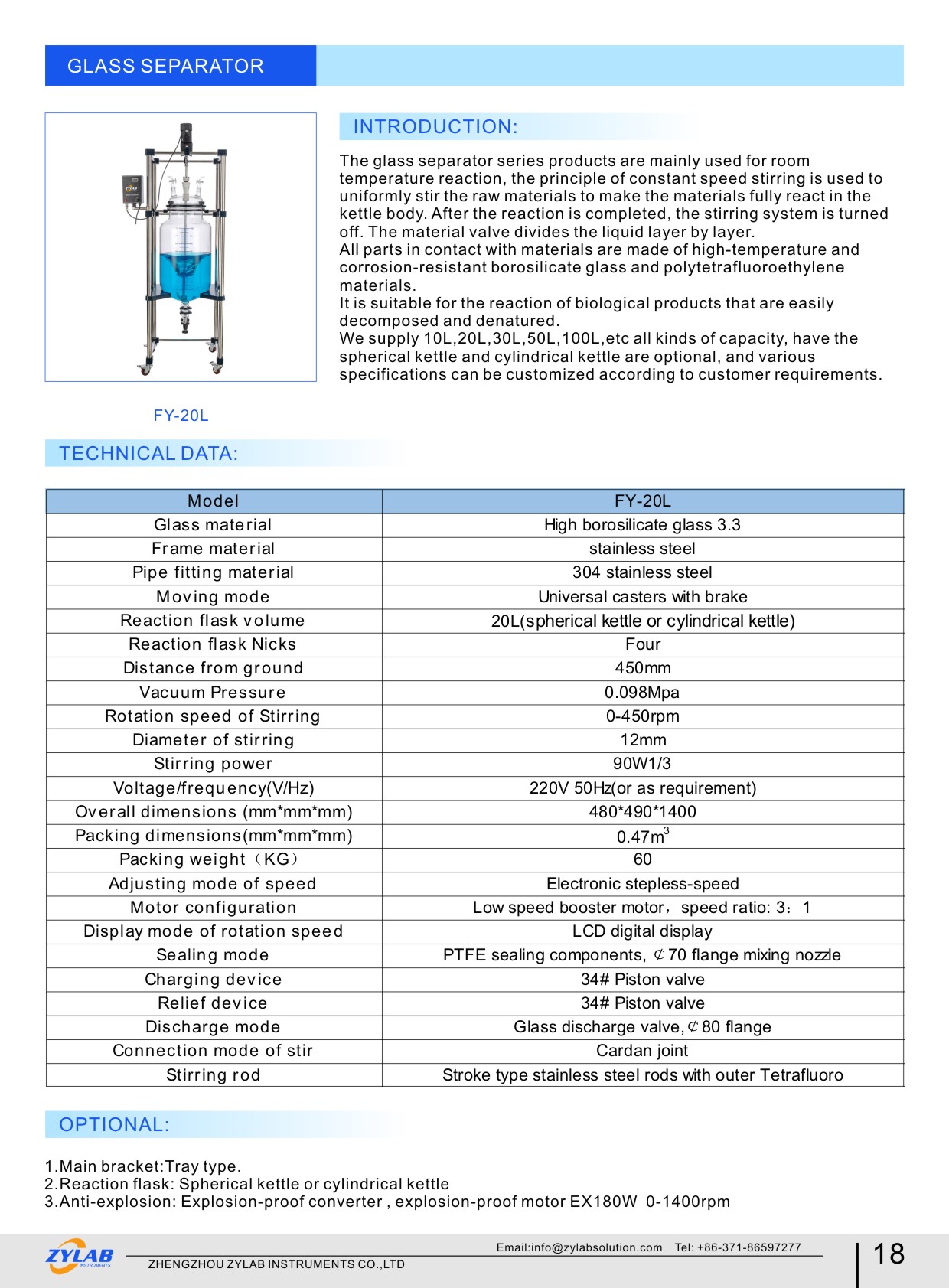
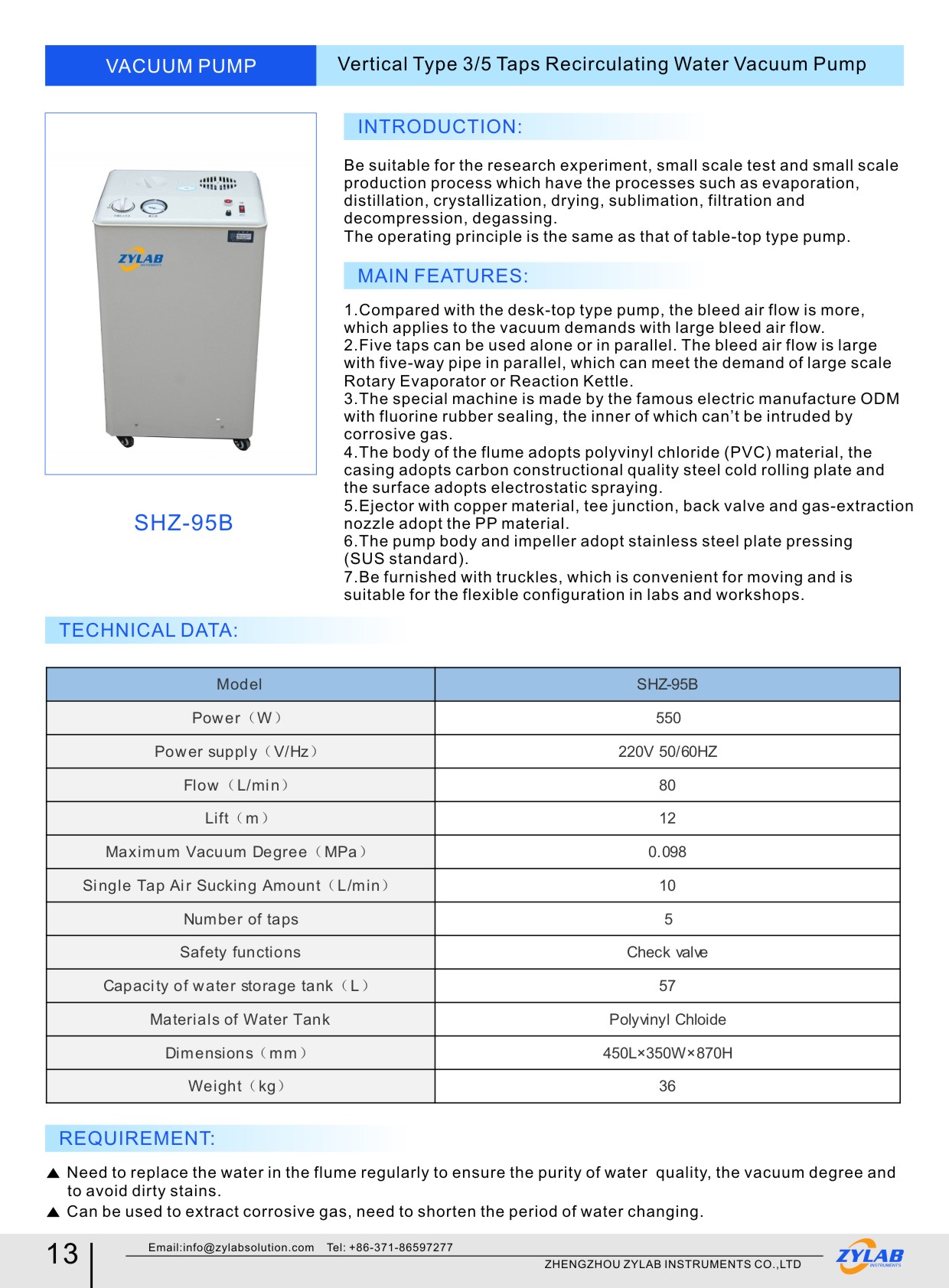
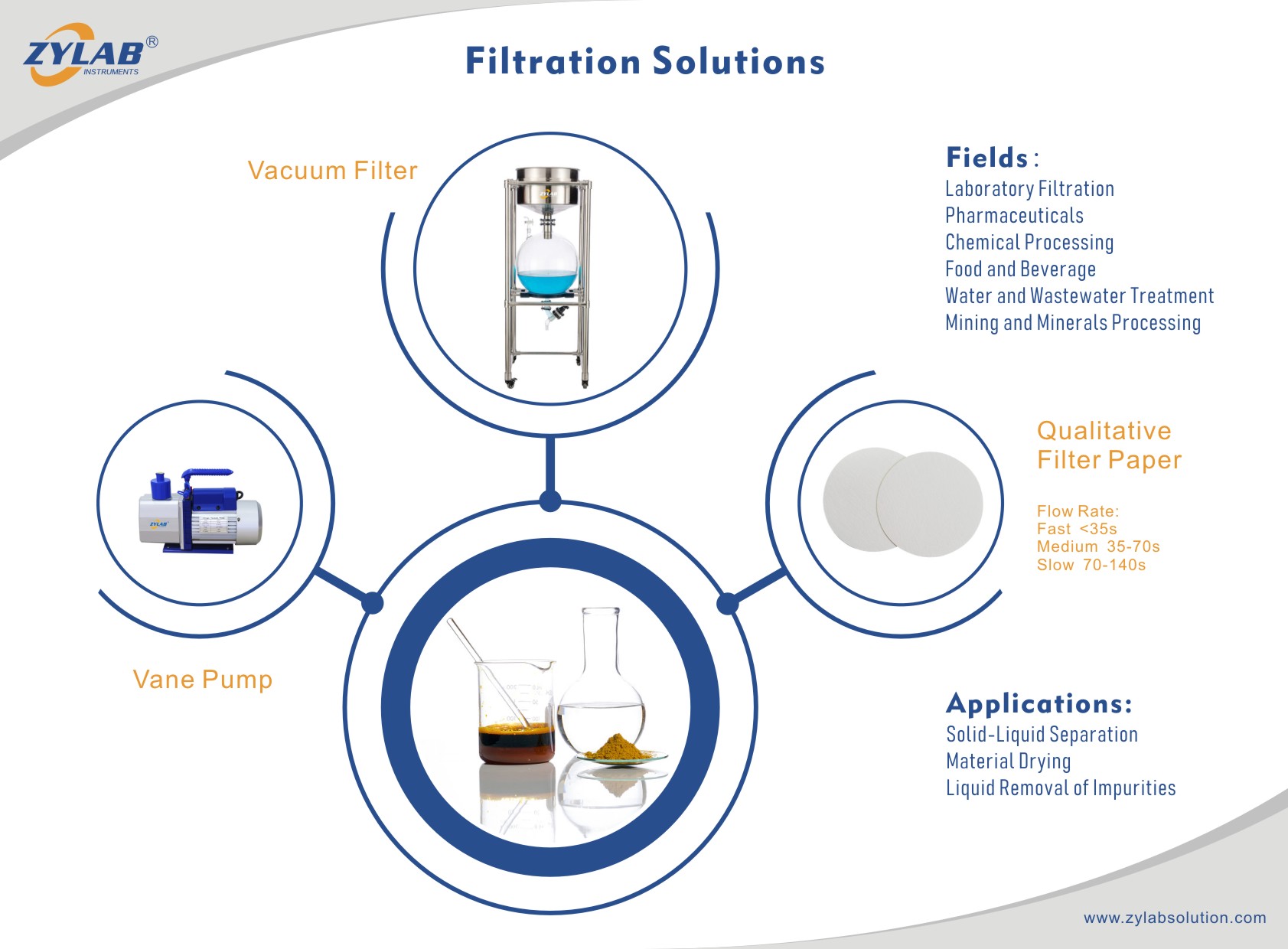
Table of Contents
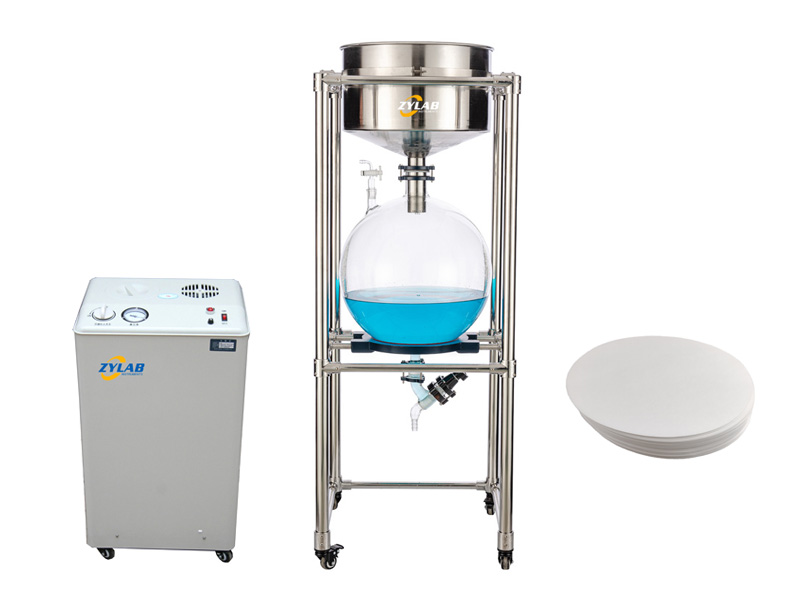
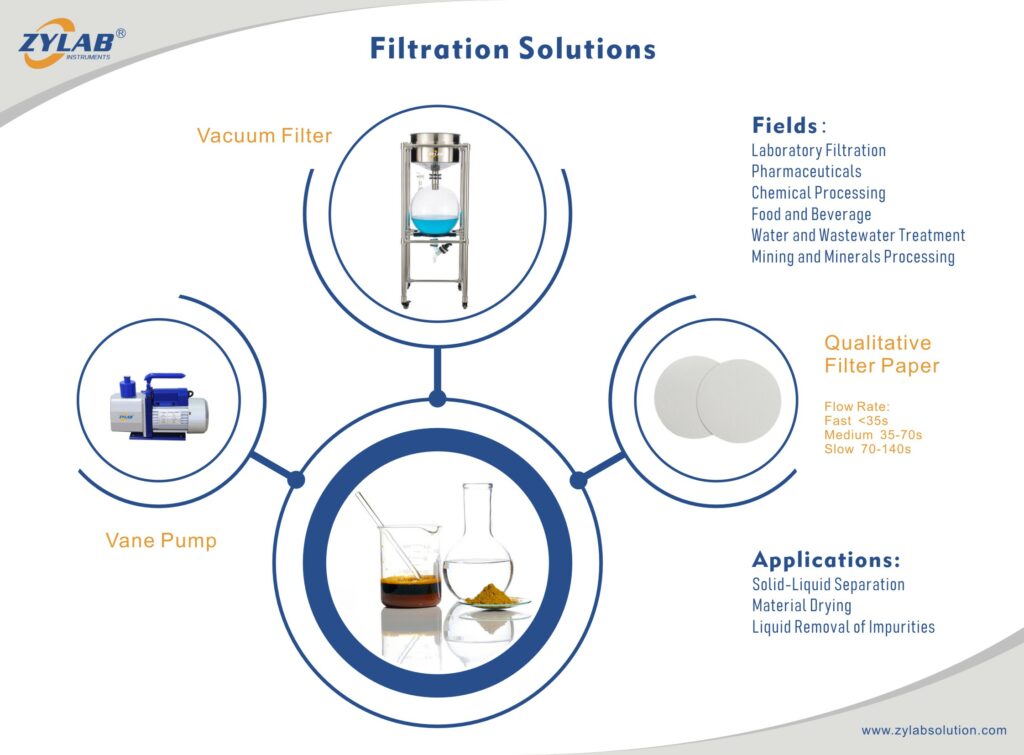
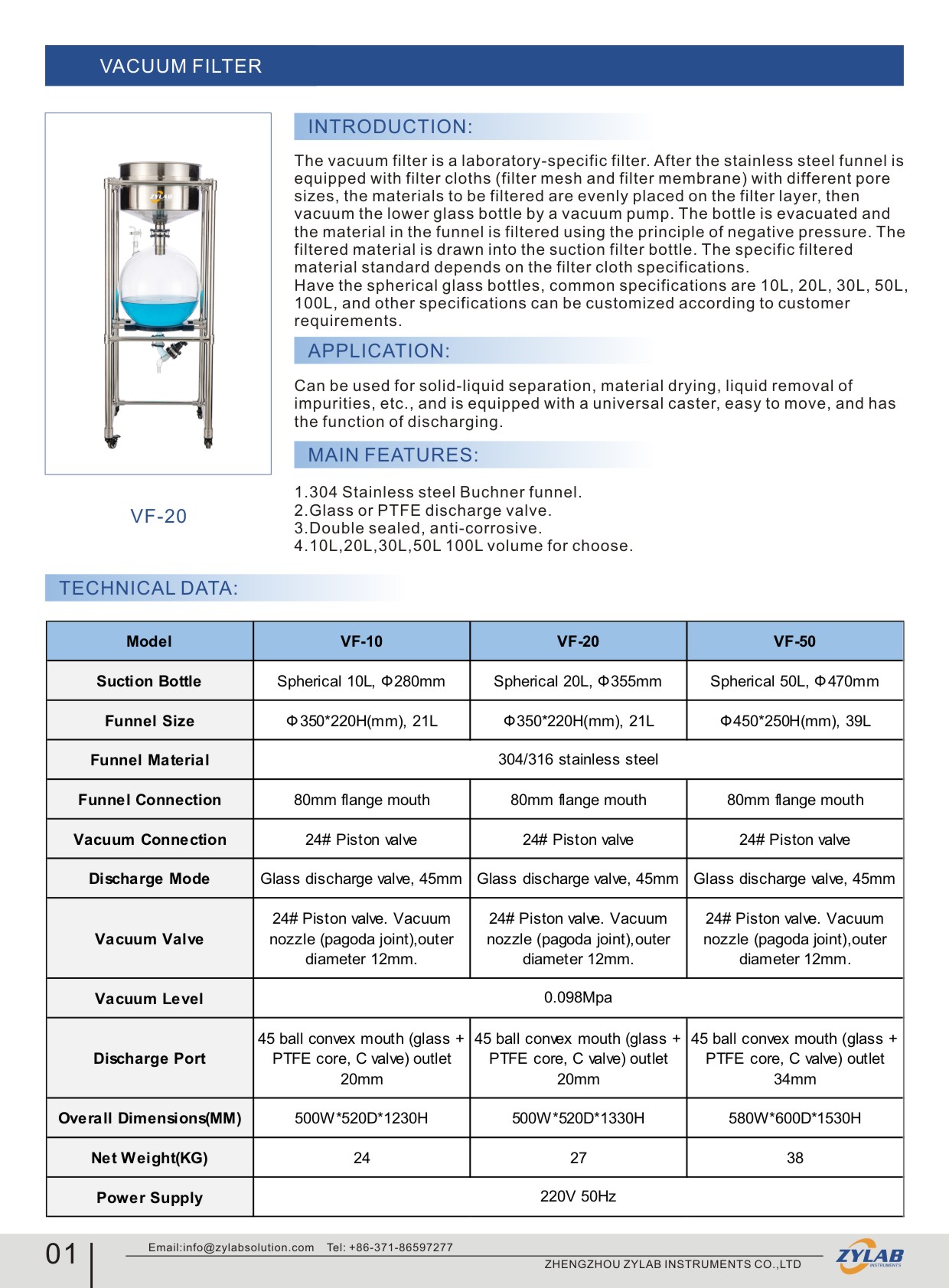
A vacuum filter is a device used to separate solid particles from a liquid or slurry by applying a vacuum to draw the liquid through a filter medium.
It is a widely used tool in various industries and laboratories for liquid-solid separation processes, including filtration, clarification, and dewatering.
Work Process
1. A liquid-solid mixture, often referred to as a slurry, is introduced into the filter.
2. A vacuum is applied to one side of the filter medium, creating a pressure difference that draws the liquid through the medium.
3. The solid particles are trapped on the surface or within the filter medium while the clarified liquid is collected in a separate container.
4. The solid residue on the filter medium, also known as the filter cake, can be further processed or disposed of.
Applications
Chemical Processing: Used for filtering chemical solutions to separate solid precipitates or impurities from liquid components.
Pharmaceutical Production: Employed in pharmaceutical manufacturing for the filtration of drug formulations, separation of crystals, and purification of pharmaceutical products.
Environmental Analysis: Applied in environmental laboratories to filter water and air samples, aiding in the detection and analysis of pollutants.
Food and Beverage Industry: Utilized for the clarification and filtration of liquids in food and beverage production, ensuring product quality and purity.
Biotechnology and Life Sciences: Used in biotech labs for various applications, including cell culture harvesting, protein purification, and separation of biomolecules.
Mining and Metallurgy: Applied in mining processes to separate solids from liquid slurries, and in metallurgical operations for filtering metal-containing solutions.
Oil and Gas Industry: Employed in the oil and gas sector for filtering crude oil and other fluids to remove impurities and contaminants.
Wastewater Treatment: Essential in municipal and industrial wastewater treatment plants to separate solids from liquid effluents before discharge.
Laboratory Filtration: Commonly used in scientific research laboratories for general filtration purposes, sample preparation, and experimental processes.
Textile Industry: Used for the filtration of dye solutions and other chemicals in textile manufacturing processes.
Paper and Pulp Industry: Employed in paper mills for the separation of solid materials from pulp slurries during the paper production process.
Electronics Manufacturing: Utilized in the electronics industry for filtering chemicals and solvents used in the manufacturing of electronic components.
Automotive Industry: Applied in coolant filtration systems to remove impurities and contaminants from cooling fluids in vehicles.
Cosmetics Production: Used for the filtration of cosmetic formulations to ensure product quality and clarity.
Educational Demonstrations: Commonly employed in educational settings to demonstrate principles of filtration and separation processes.
How to Choose the Right Vacuum Filter
Capacity: Choose a vacuum filter with the appropriate capacity for your application, ensuring it can handle the desired volume.
Filter Medium: Select the right filter medium and material for compatibility with your liquid and solid materials.
Design and Configuration: Consider the specific design and configuration that best suits your application, whether it’s a filter flask, filter holder, or another design.
Control Features: Evaluate the control mechanisms for vacuum level and flow rate to meet your process requirements.
Maintenance and Cleaning: Assess the ease of maintenance, cleaning, and replacement of filter media.
Materials of Construction: Ensure that the materials used in the filter are compatible with the chemicals and conditions in your process.
Manufacturer Reputation: Research and select a reputable manufacturer known for quality and reliability.
FAQ
1. Can a vacuum filter separate both solid particles and microorganisms from a liquid?
Yes, some vacuum filters are designed to capture both solid particles and microorganisms, making them useful in microbiological applications.
2. Can vacuum filters be used for sterile filtration in laboratories?
Yes, vacuum filters can be equipped with sterile filter media and are commonly used for sterile filtration in laboratory settings.
3. Are vacuum filters suitable for hazardous or corrosive chemicals?
Vacuum filters can be designed with materials that are compatible with a wide range of chemicals, including hazardous or corrosive substances. It is important to select the appropriate materials based on the specific chemicals being processed.
4. How often should the filter medium be replaced?
The frequency of filter medium replacement depends on the application, the volume of material processed, and the nature of the solids and contaminants. Regular inspection and replacement are necessary to maintain efficient filtration.
5. Is it possible to recover and reuse the solid material captured by the vacuum filter?
Yes, the solid material captured by the filter, known as the filter cake, can often be recovered and further processed or reused depending on the application and material characteristics.
As a leading provider of laboratory vacuum filtration solutions, we offer a range of high-quality vacuum filters for all your laboratory needs.