Table of Contents
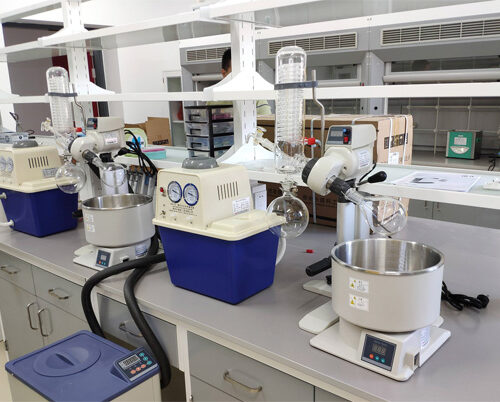
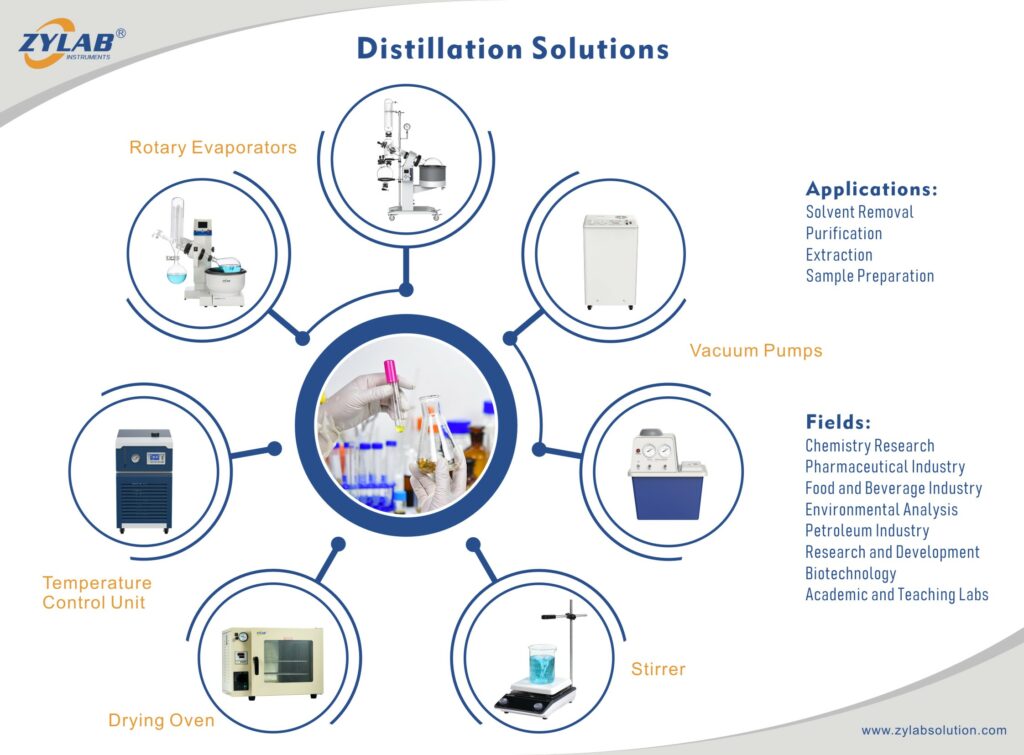
Rotary evaporator is a laboratory equipment used for liquid evaporation. It is widely used in fields such as chemistry, pharmaceuticals, and biotechnology for concentrating solutions, extracting substances, or removing solvents from liquids.
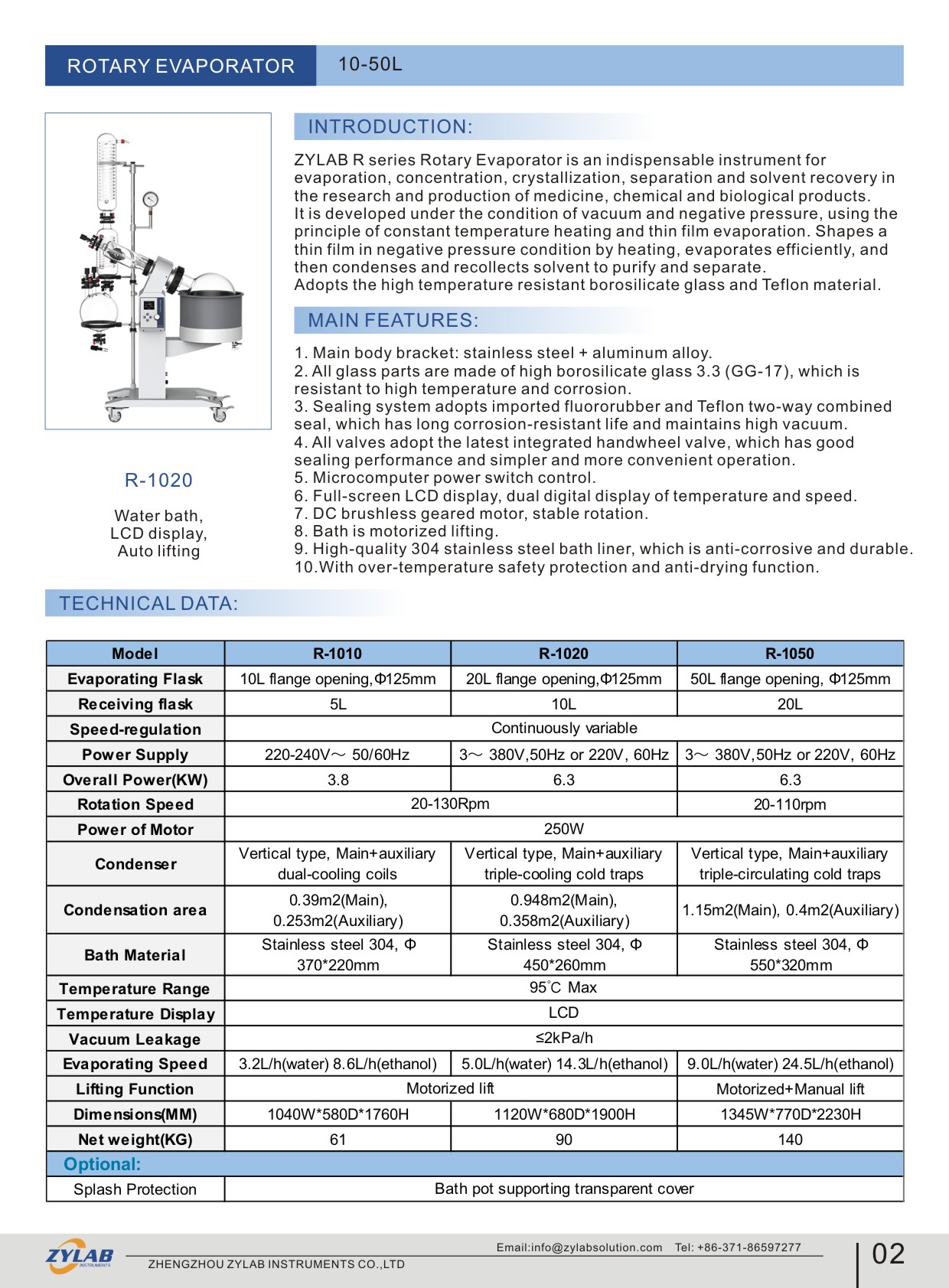
Structure of Rotary Evaporator
Container: A rotary evaporator typically consists of a cylindrical container with a heating element or heating jacket inside to provide the necessary heat for evaporation.
Rotating Mechanism: An evaporating flask is mounted on a rotating mechanism, allowing it to rotate around a horizontal axis. This rotational movement helps in forming a liquid film, improving the uniformity of evaporation.
Heating System: The bottom of the container is equipped with a heating jacket or heater to provide heat energy, allowing the liquid sample to evaporate and form a thin film.
Vacuum System: Connected to a vacuum pump, the vacuum system reduces the pressure inside the system, lowering the liquid’s boiling point and facilitating evaporation.
Condenser: Positioned above the container, the condenser is used to condense the evaporated substance back into liquid form.
Collection System: The liquid condensed after evaporation flows through a pipeline into a collection bottle for subsequent processing or analysis.
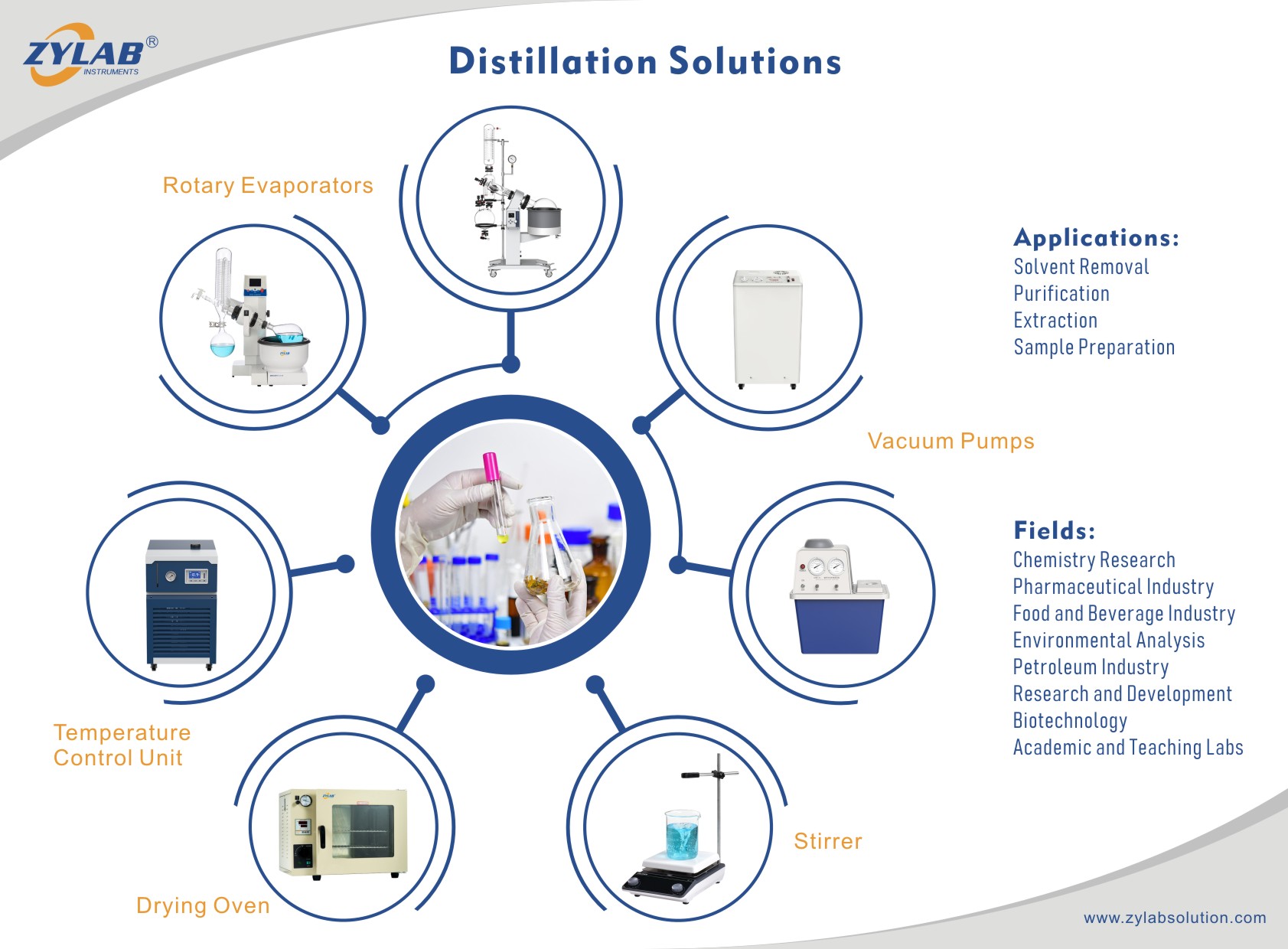
Main Applications of Rotary Evaporator in Different Industries
Pharmaceutical Industry: Rotary evaporators are commonly used in pharmaceutical processes for concentrating drug solutions, separating and extracting compounds. They play a crucial role in drug preparation and synthesis of intermediates.
Chemical Industry: In chemical production, rotary evaporators are employed to handle solutions from chemical reactions, remove solvents, and concentrate and recover valuable compounds. They hold significance in organic synthesis and solvent recovery.
Food Industry: In food processing, rotary evaporators are often used to concentrate juices, plant extracts, flavors, and seasonings. They contribute to increasing product concentration, improving taste, and preserving freshness.
Environmental Engineering: Rotary evaporators are used in the treatment of wastewater to concentrate dissolved substances, making it more effective for subsequent processing. This is beneficial in environmental engineering and water treatment.
Petroleum Industry: In the petrochemical field, rotary evaporators are utilized for processing crude oil and extracting useful components. They aid in separating different components in petroleum to meet the needs of petrochemical production.
Chemical Laboratories: In the research and development phase, rotary evaporators are common equipment in laboratories for tasks such as concentration, extraction, and compound separation.
Biotechnology: In the field of biotechnology, rotary evaporators are used to handle biological samples, concentrate biological specimens, and extract organic solvents.
Application of Rotary Evaporator in Recycling of Used Batteries
Organic Solvent Recovery: Some liquid components in used batteries may contain organic solvents, such as electrolyte solutions. Rotary evaporators can be used to evaporate these organic solvents from the waste liquid, facilitating their recovery and reuse.
Concentration of Electrolyte: The electrolyte in used batteries is typically valuable, and rotary evaporators can be employed to concentrate the electrolyte, making it easier to recover and reuse.
Separation of Hazardous Substances: Used batteries may contain toxic metal ions, acidic electrolytes, etc. Rotary evaporators can separate these hazardous substances by evaporating the liquid, thereby reducing environmental impact.
Application of Rotary Evaporator in Wastewater Treatment
Concentration of Wastewater: Wastewater often contains various organic and inorganic substances along with a large amount of water. Rotary evaporators can evaporate the water content from wastewater, concentrating it. This aids in reducing the volume of wastewater, lightening the environmental burden, and improving the efficiency of subsequent treatment steps.
Solvent Recovery: If wastewater contains organic solvents, rotary evaporators can be used to evaporate and recover these solvents, contributing to cost reduction and environmental pollution reduction.
Treatment of High-Concentration Wastewater: Some wastewater may have high concentrations of dissolved substances, making traditional wastewater treatment methods challenging. Rotary evaporators can effectively handle high-concentration wastewater by evaporating water, concentrating the dissolved substances, making subsequent treatment and disposal easier.
Separation of Solid Waste: Suspended solids or particulate matter in wastewater can be concentrated through the action of rotary evaporators, making it easier for subsequent separation and treatment. This helps reduce the amount of solid waste in wastewater.
Suitable for High Salinity Wastewater: Traditional treatment methods may be less effective for high salinity wastewater. Rotary evaporators can efficiently handle such wastewater by reducing salt concentration through water evaporation.
Key Considerations for Choosing Rotary Evaporator
Sample Properties: Consider the nature of the liquid samples to be processed. Different rotary evaporators may be suitable for different solvents, solute concentrations, viscosities, etc. Ensure that the selected equipment can handle the target samples.
Processing Scale: Depending on the volume of samples to be processed, choose a rotary evaporator with an appropriate scale. Laboratory-scale and industrial-scale equipment may vary significantly.
Heating Method: Rotary evaporators come with different heating methods, such as oil bath, electric heating, etc. Choose the appropriate heating method based on experimental conditions and sample characteristics.
Rotational Speed Control: Some applications may require precise control of the rotation speed to ensure the uniformity of the formed film. Therefore, selecting equipment with adjustable rotation speed may be advantageous.
Vacuum System: If dealing with heat-sensitive substances, having a robust vacuum system is crucial. The vacuum system helps lower the liquid’s boiling point, facilitating the evaporation process.
Condenser Design: Different condenser designs can accommodate various applications. Some applications may require special condenser forms to ensure efficient liquid condensation.
Control System: Advanced control systems provide more accurate temperature and rotation speed control, enhancing experiment stability and repeatability.
Material Selection: Ensure that the construction materials of the rotary evaporator meet the requirements of the samples, especially in the presence of corrosive or organic solvents.
Safety: Consider the safety features of the equipment, such as overheating protection, explosion-proof design, etc., to ensure the safety of operators and the experimental environment.
Brand and Manufacturer: Choose reputable brands and manufacturers, as their products typically adhere to higher quality and performance standards, along with better after-sales service.
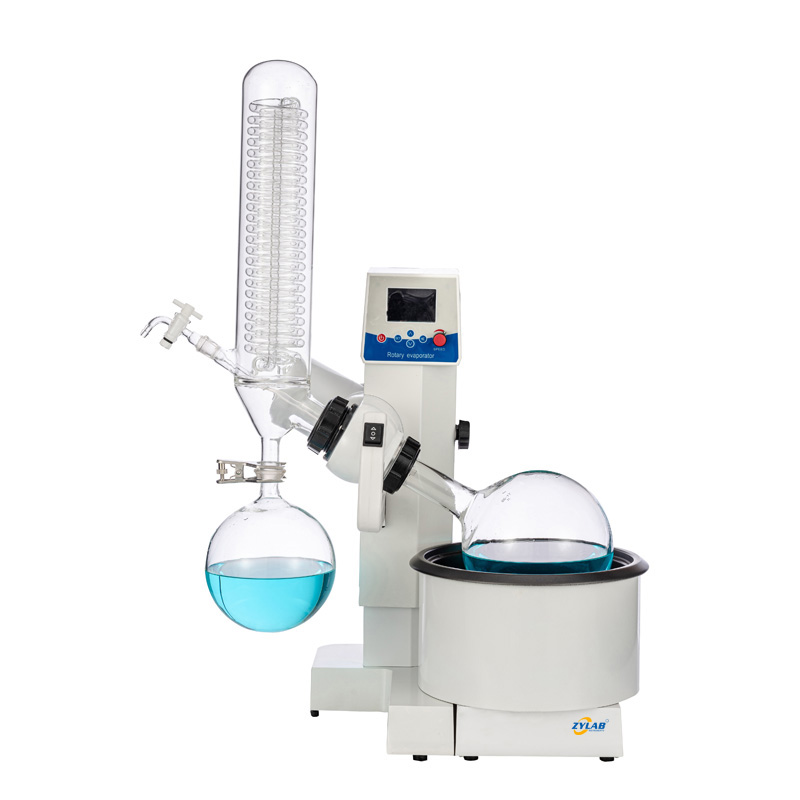
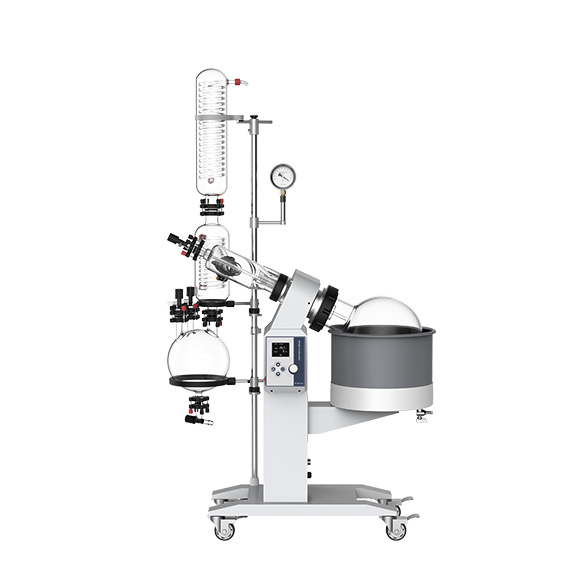
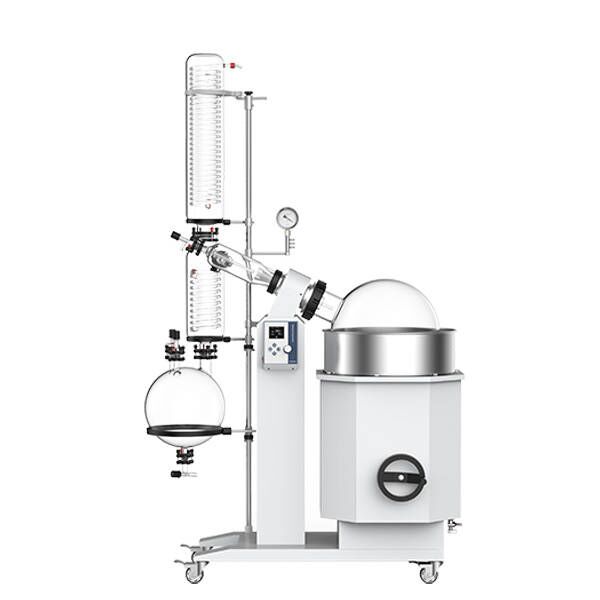
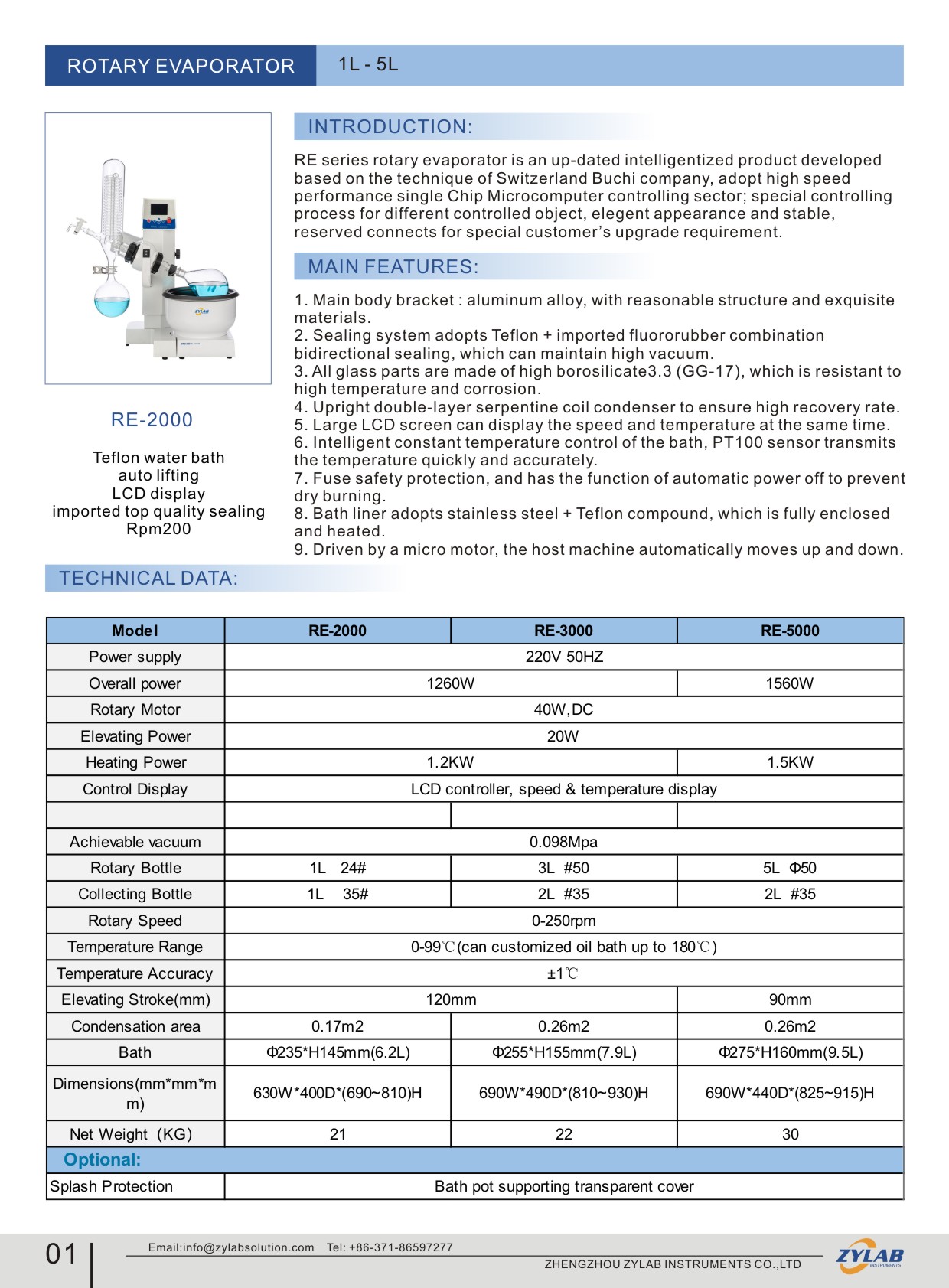
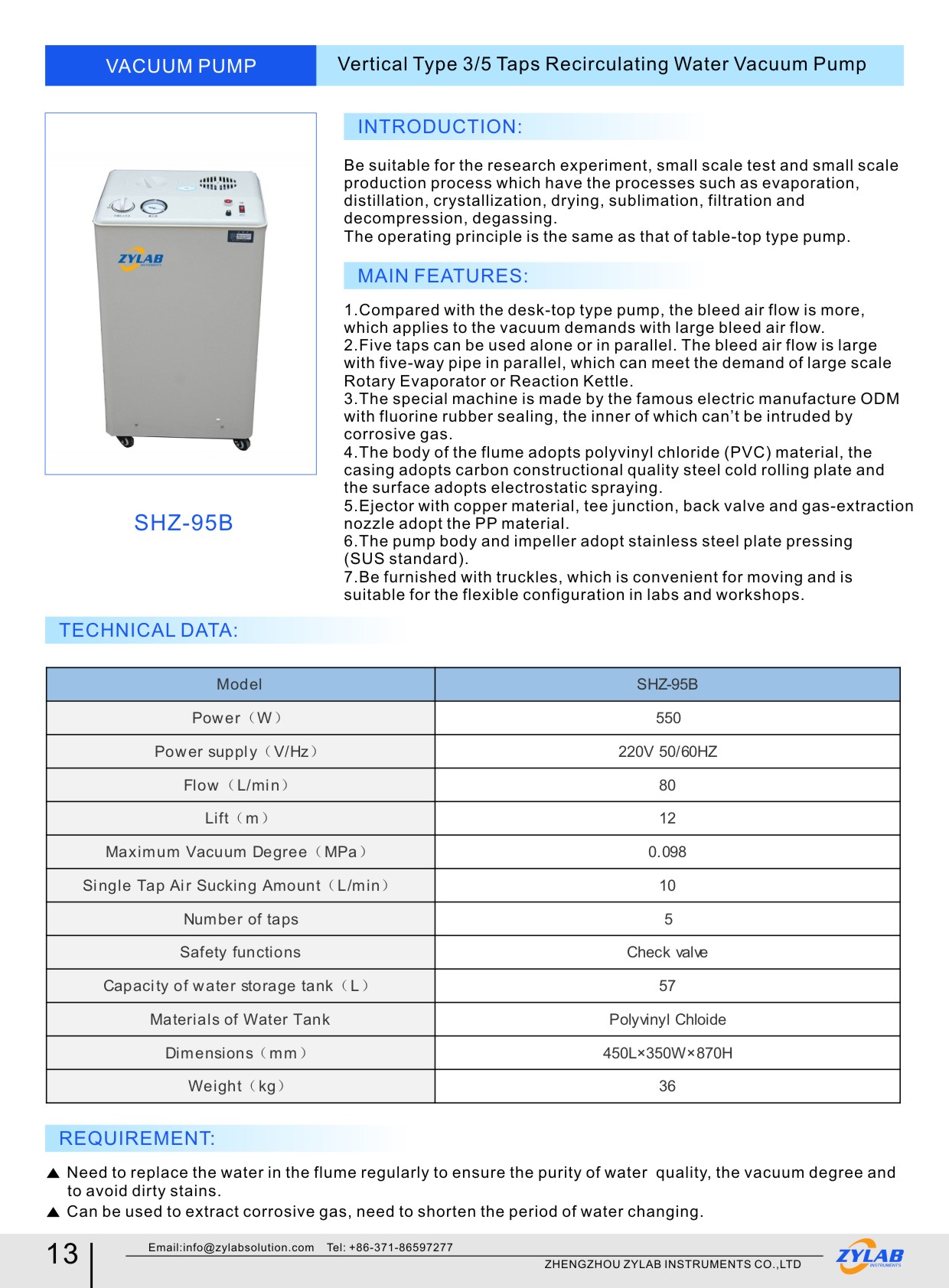
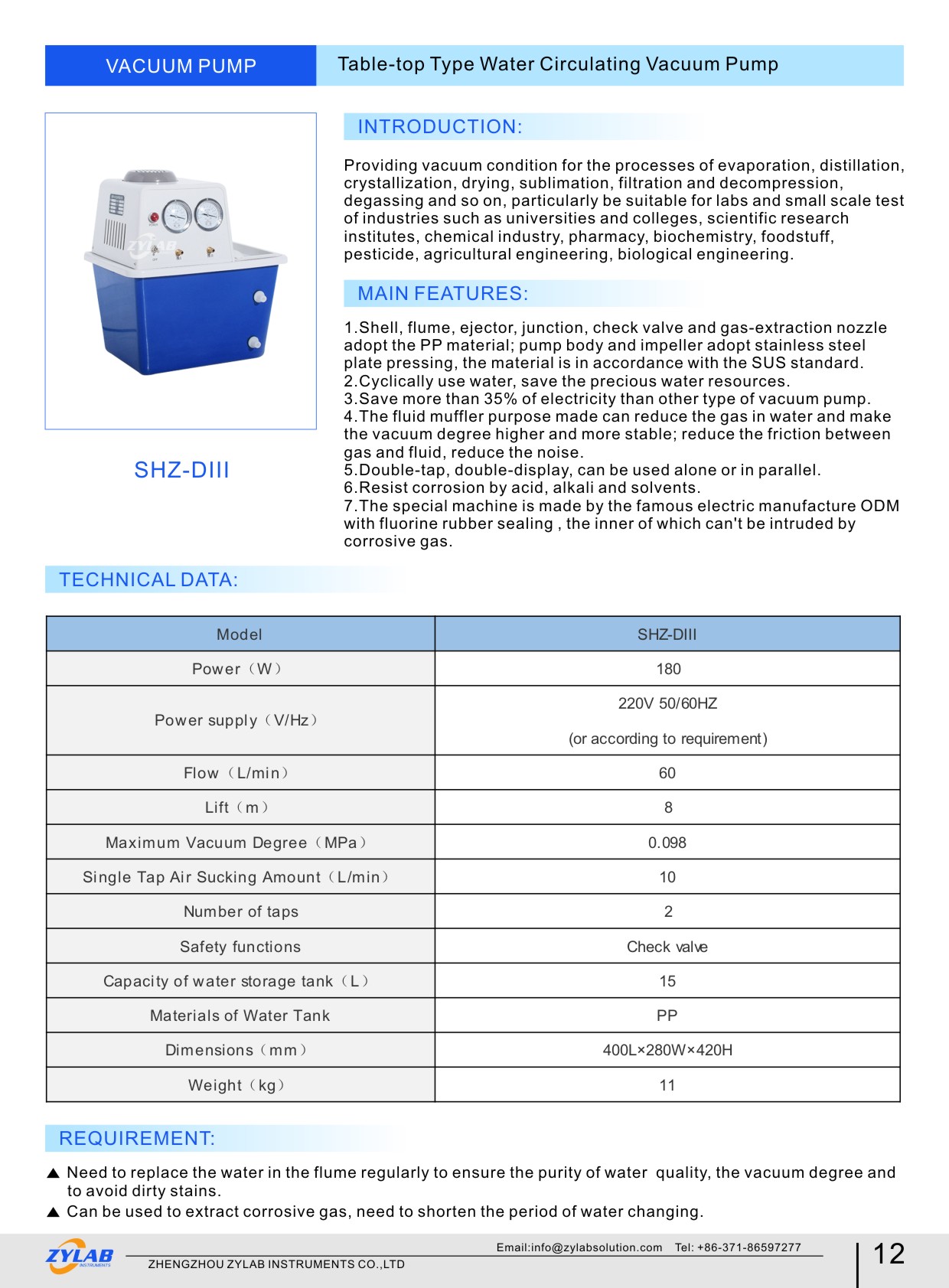
Here are some rotary evaporators recommended by ZYLAB for your reference:
When selecting a rotary evaporator, it is advisable to assess based on specific experimental or industrial needs. If you have any questions, please contact our technical personnel for professional advice.
FAQ
Q: What types of samples can be processed using a rotary evaporator?
A: Rotary evaporators are capable of processing a wide range of sample types, including volatile and semi-volatile compounds, as well as complex mixtures.
Q: How long does it take to evaporate a sample using a rotary evaporator?
A: The time required to evaporate a sample using a rotary evaporator depends on a variety of factors, including the size of the sample, the temperature, and the vacuum pressure. Generally, evaporation times can range from several minutes to several hours.
Q: Is a rotary evaporator safe to use?
A: Yes, rotary evaporators are designed with safety in mind, featuring a range of built-in safety features, including automatic shut-off and overheat protection. However, it is essential to follow manufacturer instructions and best practices for safe and effective operation.
Q: Can I use a rotary evaporator for large-scale production?
A: Yes, rotary evaporators are capable of handling large-scale production. However, it is important to select a model that is appropriate for the size and type of production required.
Q: What is the difference between a rotary evaporator and a distillation apparatus?
A: While both rotary evaporators and distillation apparatus are used for separation and purification of compounds, rotary evaporators offer greater control and efficiency in the process due to their ability to rotate the sample, control temperature and vacuum pressure, and optimize separation.
Q: How do I clean and maintain my rotary evaporator?
A: Regular cleaning and maintenance of your rotary evaporator is essential to ensure long-lasting performance and safety. Follow manufacturer instructions for proper cleaning and maintenance, including regular inspection of parts and components, and timely replacement of worn or damaged parts.