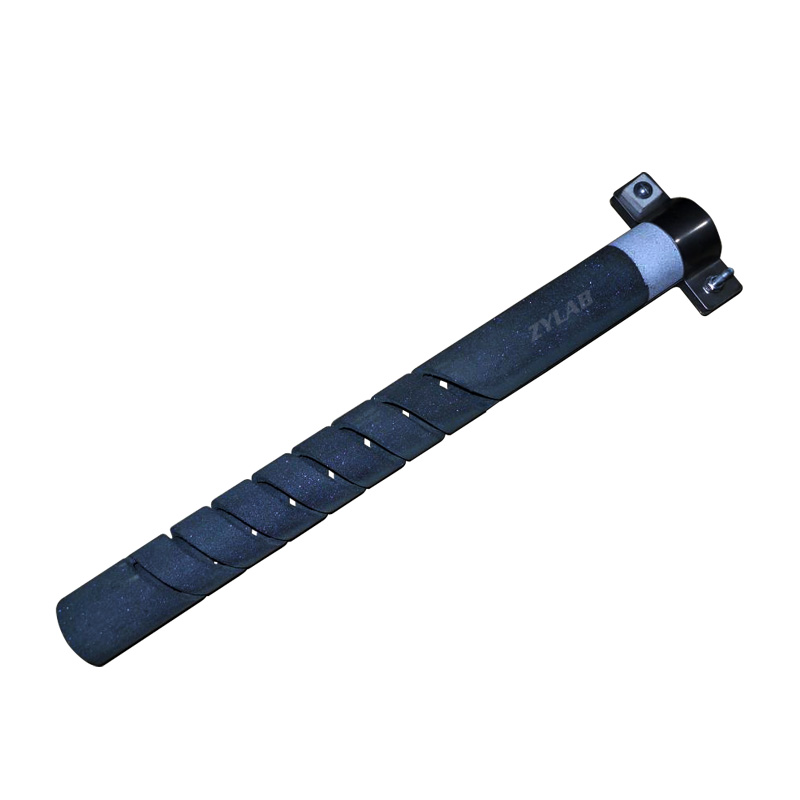
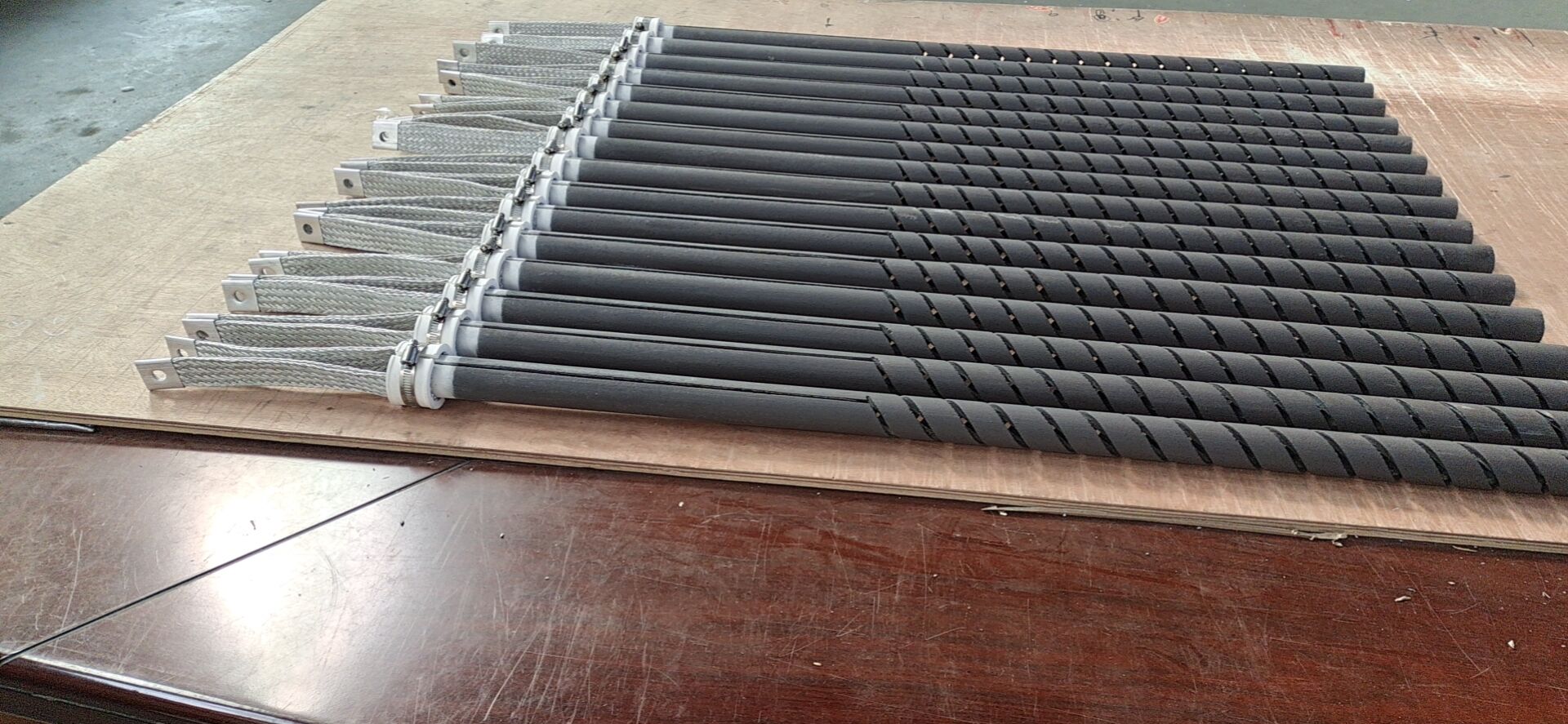
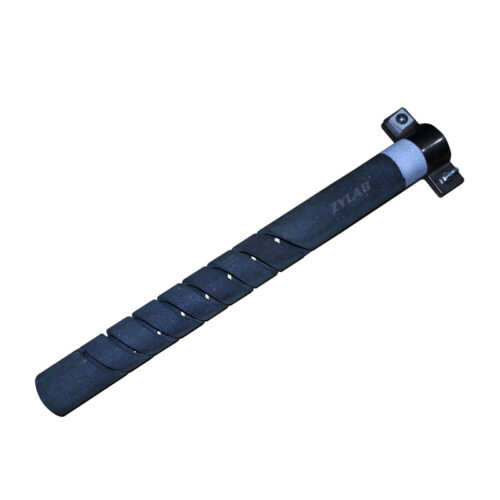
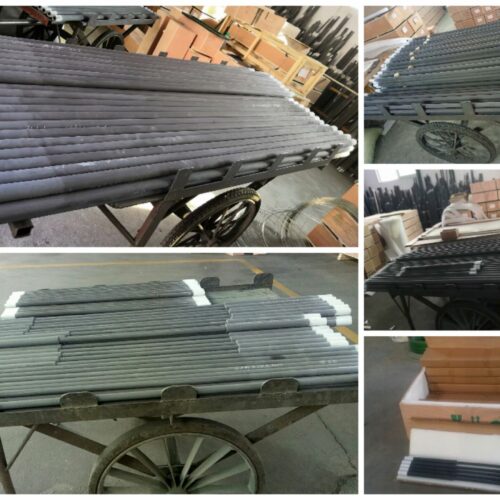
Double Spiral Type SiC Heater
General Description:
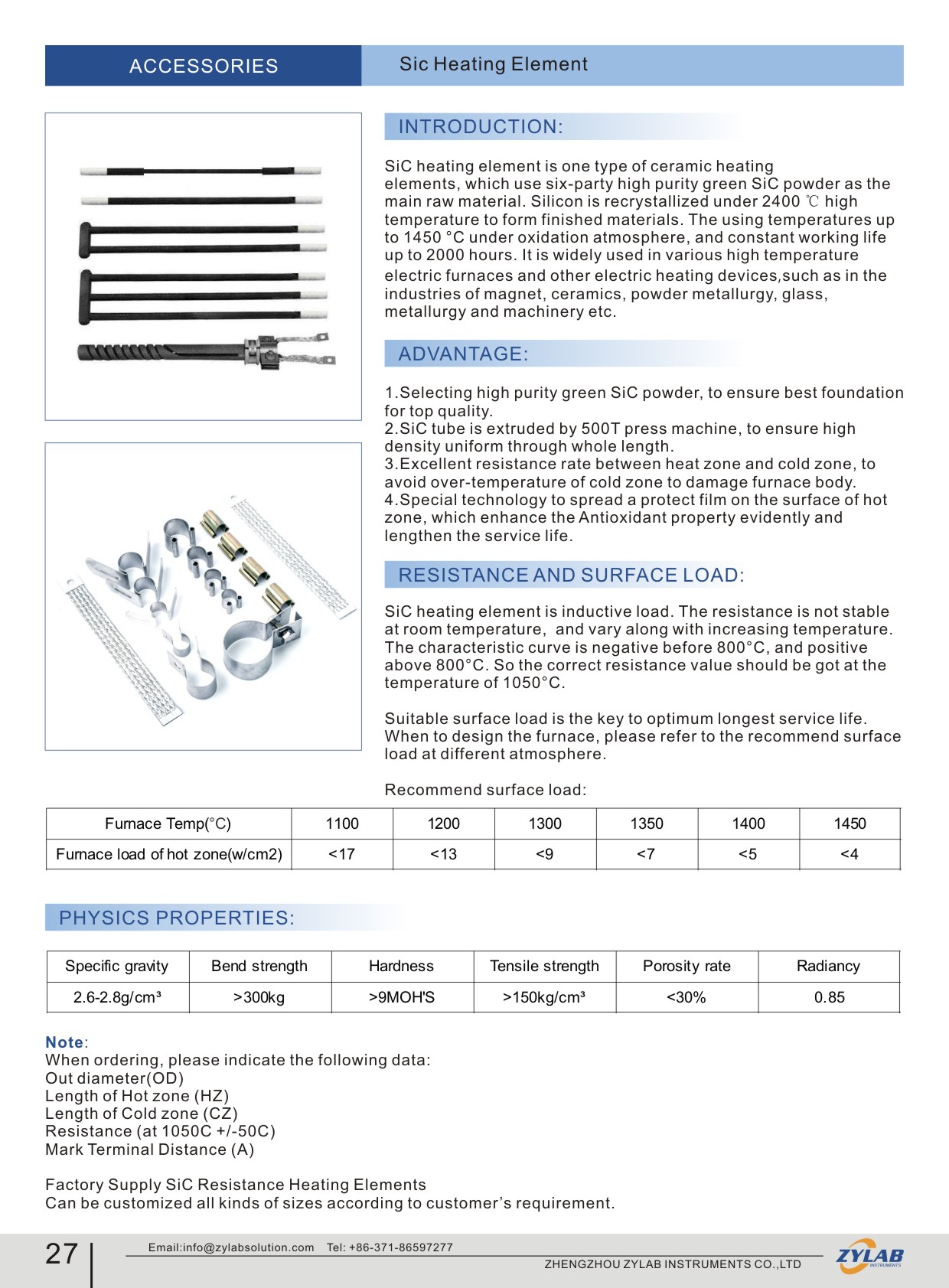
SiC Heater is one type of ceramic heating elements, which use six-party high purity green SiC powder as the main raw material. Silicon is recrystallized under 2200 ℃ high temperature to form finished materials. The using temperatures up to 1450 °C under oxidation atmosphere, and constant working life up to 2000 hours. It is widely used in various high temperature electric furnaces and other electric heating devices, such as in the industries of magnet, ceramics, powder metallurgy, glass, metallurgy and machinery etc.
Advantages of ZYLAB SiC Heater:
1. Selecting high purity green SiC powder, to ensure best foundation for top quality.
2. SiC tube is extruded by 500T press machine, to ensure high density uniform through whole length.
3. Excellent resistance rate between heat zone and cold zone, to avoid over-temperature of cold zone to damage furnace body.
4. Special technology to spread a protect film on the surface of hot zone, which enhance the Antioxidant property evidently and lengthen the service life.
Note: When ordering, please indicate the following data:
Out diameter(OD)
Length of Hot zone (HZ)
Length of Cold zone (CZ)
Resistance (Ω)(at 1050C +/-50C)
Can be customized all kinds of sizes according to customer’s requirement.
Detail Applications:
Silicon Carbide (SiC) heating elements(heaters) find applications across various industries due to their unique properties and advantages. Some common applications include:
High-Temperature Furnaces
SiC heating elements are extensively used in high-temperature furnaces for processes such as sintering, annealing, brazing, and heat treatment of metals, ceramics, and other materials. They can operate at temperatures up to 1500°C (2732°F) and provide rapid heating and uniform temperature distribution within the furnace chamber.
Semiconductor Industry
SiC heating elements are crucial in semiconductor manufacturing processes, including chemical vapor deposition (CVD), physical vapor deposition (PVD), and diffusion. They provide precise and stable heating environments required for the deposition, annealing, and processing of semiconductor materials and devices.
Glass and Ceramic Industry
SiC heating elements are employed in glass melting furnaces, kilns, and ceramic production processes. They offer high-temperature stability, resistance to chemical corrosion, and long service life, making them ideal for heating glass melts, annealing glass products, and firing ceramic materials.
Heat Treatment and Metallurgy
SiC heating elements are used in heat treatment processes for hardening, tempering, and annealing of metals and alloys. They provide rapid heating and cooling rates, uniform temperature distribution, and precise temperature control, essential for achieving desired material properties and microstructures.
Powder Metallurgy
SiC heating elements find applications in powder metallurgy processes, including powder compaction and sintering. They provide the high temperatures required for consolidating powdered metals into dense, solid components while minimizing oxidation and contamination.
Laboratory and Research
SiC heating elements are commonly used in laboratory and research environments for materials synthesis, chemical reactions, and thermal analysis experiments. They offer precise temperature control, rapid heating rates, and compatibility with various atmospheres, essential for conducting controlled experiments and characterizing materials.
Environmental Testing
SiC heating elements are employed in environmental chambers for simulating extreme temperatures and thermal cycling conditions. They provide reliable and stable heating for testing the performance and durability of materials and components under harsh environmental conditions, such as those encountered in aerospace, automotive, and electronic applications.
Overall, SiC heating elements offer advantages such as high-temperature capability, rapid heating and cooling, uniform heating, chemical inertness, and long service life, making them indispensable in a wide range of industrial, scientific, and commercial applications.