Biochar R&D
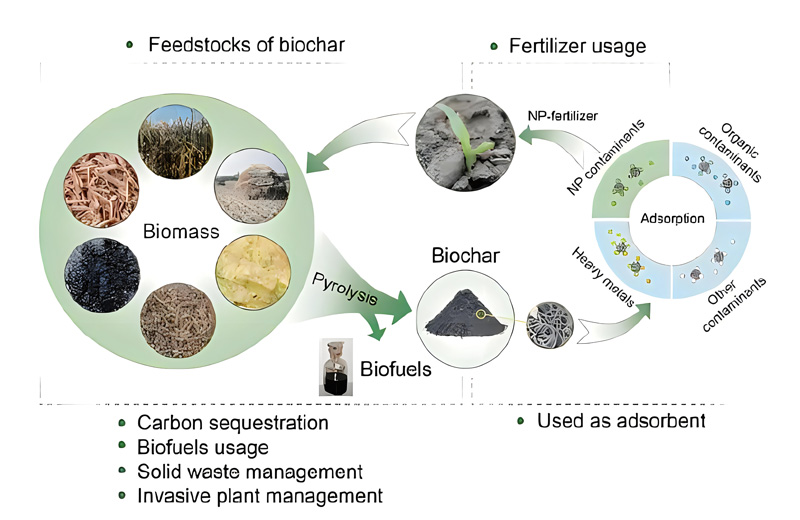
Research and development (R&D) in the field of biochar involves exploring various aspects of this carbon-rich material derived from biomass pyrolysis.
Here are some key areas of biochar R&D:
Production Methods:
Researchers are constantly refining and developing methods for producing biochar from different biomass feedstocks. This includes optimizing pyrolysis processes for efficiency, yield, and quality of biochar produced.
Characterization:
Understanding the physical, chemical, and structural properties of biochar is crucial for its application in different fields. R&D efforts focus on characterizing biochar to determine its suitability for various applications such as soil amendment, carbon sequestration, water filtration, and more.
Soil Amendment:
Biochar is widely studied for its potential as a soil amendment to improve soil fertility, structure, and water retention. Research in this area includes investigating the effects of biochar on soil microbial activity, nutrient availability, and overall soil health.
Carbon Sequestration:
Biochar has the potential to sequester carbon in soils for long periods, mitigating greenhouse gas emissions and combating climate change. R&D efforts focus on quantifying the carbon sequestration potential of biochar and understanding the factors that influence its stability in soil.
Waste Valorization:
Biochar production offers a way to valorize biomass waste streams, including agricultural residues, forestry residues, and organic waste. R&D in this area aims to identify suitable feedstocks and develop efficient processes for converting waste biomass into biochar.
Water Treatment:
Biochar can be used as a filter media for water treatment, removing contaminants such as heavy metals, organic pollutants, and nutrients from wastewater and stormwater. Research focuses on optimizing biochar properties and deployment methods for effective water treatment applications.
Biological Applications:
Biochar shows potential in various biological applications, including livestock farming, aquaculture, and bioremediation. R&D efforts explore the use of biochar as a feed additive, substrate for microbial growth, and remediation agent for contaminated soils and water bodies.
Economic Viability and Scale-up:
Research aims to assess the economic feasibility of biochar production and utilization at different scales. This includes evaluating the costs associated with biochar production, application, and potential revenue streams from its various uses.
Overall, biochar R&D is multidisciplinary, involving expertise from fields such as chemistry, agronomy, environmental science, and engineering, with the ultimate goal of harnessing the potential of biochar for sustainable agriculture, environmental remediation, and climate change mitigation.
Related Equipment Recommend:
100-1200.C
100-1200.C
100-1200.C





















