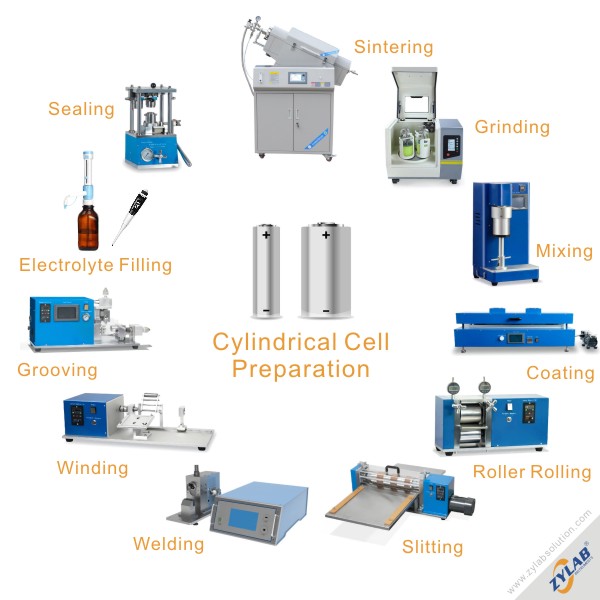
Cylindrical Cell Preparation
Cylindrical cells, another common type of rechargeable lithium-ion battery, have a different design compared to pouch cells. These cells are typically enclosed in a metal cylindrical can. Here is a general overview of the preparation process for cylindrical cells:
-
Materials and Components:
- Positive electrode (cathode) material
- Negative electrode (anode) material
- Electrolyte solution
- Separator material
- Cylindrical metal can (usually made of aluminum or steel)
- Insulating materials
- End caps with current collectors
-
Electrode Coating:
- Similar to pouch cells, the positive and negative electrode materials are coated onto metal foils. This involves a slurry coating process where a mixture of active material, conductive additives, and a binder is coated onto the foil.
-
Rolling and Winding:
- The coated positive and negative electrode foils, along with separator material, are rolled and wound into a cylindrical shape. This forms the electrode assembly.
-
Assembly into Cylindrical Can:
- The wound electrode assembly is inserted into the cylindrical metal can. The can serves as the outer casing and also acts as the current collector for one of the electrodes (usually the positive electrode).
-
Electrolyte Filling:
- The cylindrical cell is filled with the electrolyte solution. The electrolyte is a conductive solution that facilitates the movement of ions between the positive and negative electrodes during the battery’s operation.
-
Sealing:
- The cylindrical cell is sealed to prevent electrolyte leakage and maintain the internal integrity of the cell.
-
Formation:
- The assembled and sealed cylindrical cell undergoes a formation process. This involves initial charge and discharge cycles to condition the battery and optimize its performance.
-
Insulation and Packaging:
- Insulating materials are added to prevent short circuits within the cell. The cell is then often packaged in a protective outer casing.
-
Aging and Testing:
- The cylindrical cells may undergo an aging process to simulate usage conditions and evaluate their long-term performance.
- Various tests, including capacity testing, cycle testing, and safety testing, are conducted to ensure the cylindrical cells meet quality standards.
-
Final Inspection:
- A final inspection is conducted to verify that each cylindrical cell meets the specified quality and safety standards.
Basic Process of Pouch Cell Preparation:
The exact details of the cylindrical cell preparation process can vary depending on the specific battery chemistry, manufacturer, and intended application.
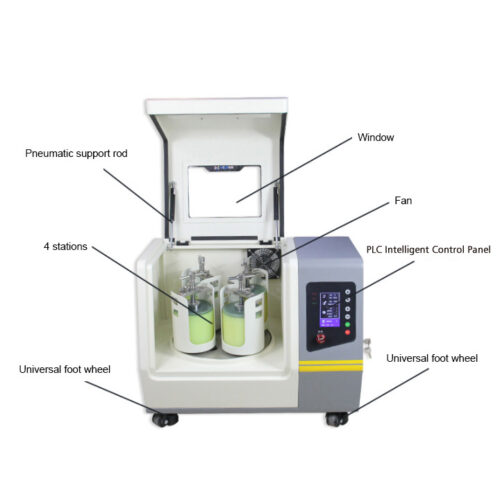
Equipment Recommend:
100-1200.C
800-1700.C
100-1200.C




















