Table of Contents
MoSi2 heating elements be widely used in such applications of sintering and heat treatment of ceramics, magnet, glass, metallurgy, refactory, etc.
Introduction
Mosi2 heating elements is a kind of resistance heating element basically made of high pure Molybdenum Disilicide.
In oxidizing atmosphere, a layer of compact quartz protective film is formed on the surface of MoSi2 element owing to the high temperature combustion, which prevent MoSi2 from continuously oxidizing.
In oxidizing atmosphere, its Max temperature can reach 1800.C, and its applicable temperature is 700-1700.C(can’t be used in 400-700.C for a long time, otherwise, it will be powdered and damaged due to strong oxidizing action in low temperature).
The most common shape is U. It is widely used for industrial and laboratory furnaces.
Type of MoSi2 Heating Elements

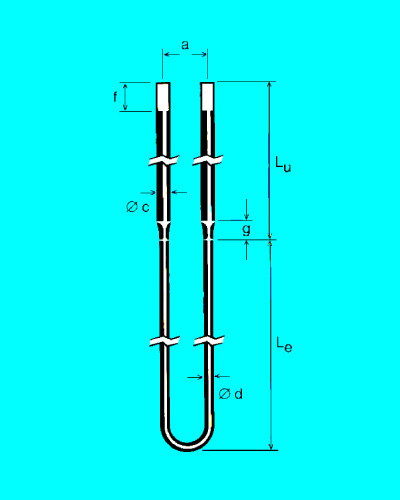
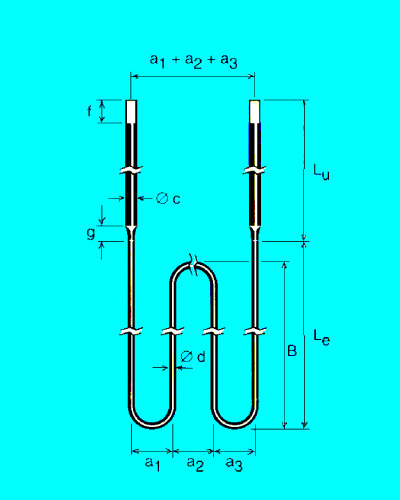
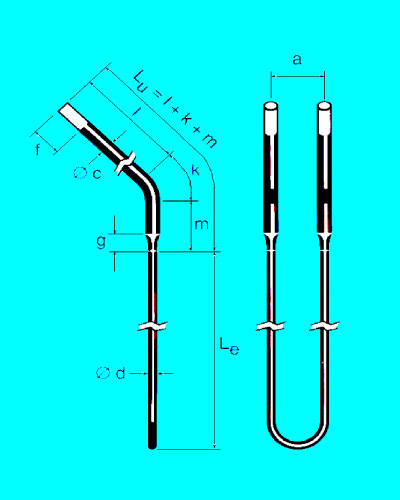
Main Specification
M1700 type (d/c): dia3/6, dia4/9, dia6/12, dia9/18, dia12/24
M1800 type (d/c): dia3/6, dia4/9, dia6/12, dia9/18, dia12/24
How to Choose MoSi2 Heating Elements
MoSi2 heating element life-cycles depend heavily on the environment in which the heat treating is done.
Switching between reducing environments and oxidizing environments can lower the lifetime of the heating element. Because the reducing environment removes the protective silica layer that forms on the surface. This layer protects the heating element from internal oxidation. Before use, MoSi2 heating elements are intentionally oxidized to produce the silica layer.
For Brother Furnace’s 1700 type MoSi2 heating elements, you can run at 1600C for hundreds to several thousands of hours in the air with somewhat standard mosi2 elements.
But At 1700C, you might typically last only a few hundred hours in a well-insulated lab size furnace. So if your working temperature is 1700C, please choose our 1800 type MoSi2 heating elements.
MoSi2 elements typically fail by gradual thinning due to oxidation losses. When they drop to a certain thickness, the power density capability is exceeded and they heat up hotter in the thin area than a thick area and burn out.
The thinning is also exacerbated by grain growth of the MoSi2, as the grains grow due to the high temps you can sometimes see an orange peel look on the surface.
We typically add small amounts of other elements to MoSi2 to help prevent grain growth. Some elements are better than others in this respect and we have different grades for different conditions.
Note: MoSi2 elements also do not prefer to be turned on and off frequently, using them at lower temperatures (400-700C) can actually speed up oxidation thinning.
How to Extend MoSi2 Heating Elements Life
1. MoSi2 heating element is only suitable for use in air or inert gas environments. Other active gas, such as H2, Cl2, and SO2, will damage the heating element.
2. Please don’t use the furnace at 400 – 700℃ temperature range for a long time because the MoSi2 heating element will be easy to be oxidized in the temperature range.
3. MoSi2 heating element is very brittle. Please pay great attention during moving and handling. Also, please avoid rapid heating and cooling to avoid the heating element broken. Max. 10℃/min heating or cooling rate is suggested.
4.Please check the heating element every 3 months to see if they are in good connecting condition. If the connection gets loose, please open the over and tighten it properly.
Properties
Physics Properties
| Volume Density | Bend Strength | Vickers Hardness | Porosity Rate | Water Absorption | Hot Extensiblity |
| 5.5-5.6kg/cm³ | 15-25kg/cm³ | (HV)570kg/mm³ | 7.40% | 1.20% | 4% |
Chemical Properties
High Temperature Oxidation Resistance
Under high temperature oxidation atmosphere, a dense Shi Ying ( SiO2) protective layer is formed on the surface of the element to prevent MoSi2 from further oxidation.
When the element temperature is greater than 1700 ℃ and the SiO2 protective layer with melting point of 1710 ℃ melts, SiO2 melts into droplets and loses its protective effect due to surface tension. When the element is used again in an oxidizing atmosphere, the SiO2 protective layer is regenerated.
It must be pointed out that the components should not be used for a long time in the range of 400 -900 ℃. Otherwise, the element will be pulverized due to the strong row oxidation at low temperature.
The Max Temperature of Elements in Different Atmosphere
| Atmosphere | Max element temperature | |
| 1700 type | 1800 type | |
| Air | 1700℃ | 1800℃ |
| Nitrogen | 1600℃ | 1700℃ |
| Argon & Helium | 1600℃ | 1700℃ |
| Hydrogen | 1100-1450℃ | 1100-1450℃ |
| N2/H2 95/5% | 1250-1600℃ | 1250-1600℃ |
| General applications | Mainly used in industrial heat treatment furnaces, sintering furnaces, foundry furnaces, glass melting furnaces, smelting furnaces. | Mainly used in experimental furnace, testing equipment and high temperature sintering furnace. |
Electric Properties of Elements
Resistance Properties
The resistivity of MoSi2 heating elements increases rapidly with the increase of temperature. Under normal operation, the resistance of the element generally does not change with the length of time. Therefore, new and old components can be mixed.
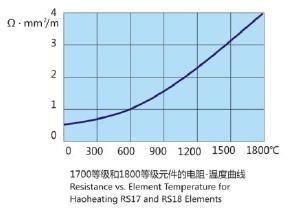
Surface Load
According to the structure of the furnace, the correct choice of the surface load of the components in terms of atmosphere and temperature is the key to achieving the best component life.
The right diagram shows the relationship between the furnace temperature, component temperature and surface load of the component radiation without obstruction, and the shaded part is the commonly used surface load – temperature range.
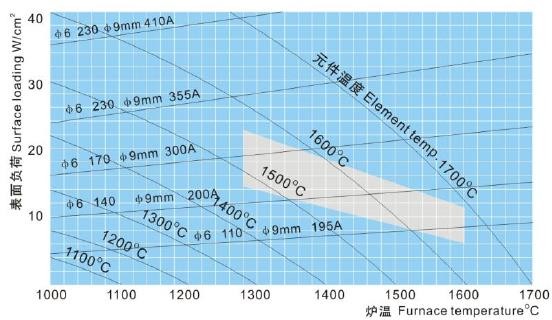
Recommend Surface Load
| Furnace Temp | 1400 | 1500 | 1600 | 1650 | 1700 |
| Surface load of hot zone (w/c ㎡) | <18 | <15 | <12 | <10 | <8 |
Installation of MoSi2 Heating Elements
Vertically Hanging
MoSi2 heating elements is brittle at normal temperature and plastic at high temperature. Therefore, the best installation method for U – shaped components is vertical suspension. The components are suspended vertically on the roof by fixing clamps ( porcelain clamps ).
The purpose of this installation is to avoid adding mechanical stress to the heating end of the element, otherwise it will easily cause the element to break.
Element Holder
The weight of the whole component is borne by the fixing clip, and the position of the component is also determined by it. Therefore, it must be carefully installed to ensure the vertical suspension of the components.
In order to avoid local overheating, the conical part at the lower end of the element must extend into the furnace.
Connection Strap
The connecting wires of the contact elements are made of aluminum woven tape or multi-layer aluminum foil. Outside the clip only plays a tightening role, not to conduct electricity. The end of the wire is connected to the bus bar.
In order to prevent stress from spreading to the component, the length of the wire should be slightly larger than the linear distance between the component and the bus bar.
The screw on the chuck should not be screwed too tightly at one time when installing the component, but tightened again when the component rises to high temperature because the component has a certain plasticity and is not easy to break. The temperature of the chuck part should not be higher than 200 ℃.
Therefore, the contact voltage between the chuck wire and the component should be less than 0.1V . In order to prevent radiant heat from reaching the chuck, the distance between the lower end of the chuck and the upper end of the brick should not be less than 50 mm. In order to avoid damage, Φ 6 / 12 mm components cannot use 170A current for a long time, φ 9 / 18 mm components cannot use 300A current for a long time.
Accessories of Element
Standard accessories for MoSi2 heating elements include element fixing clips and two aluminum woven connecting strips with clips or aluminum foil connecting strips with clips.
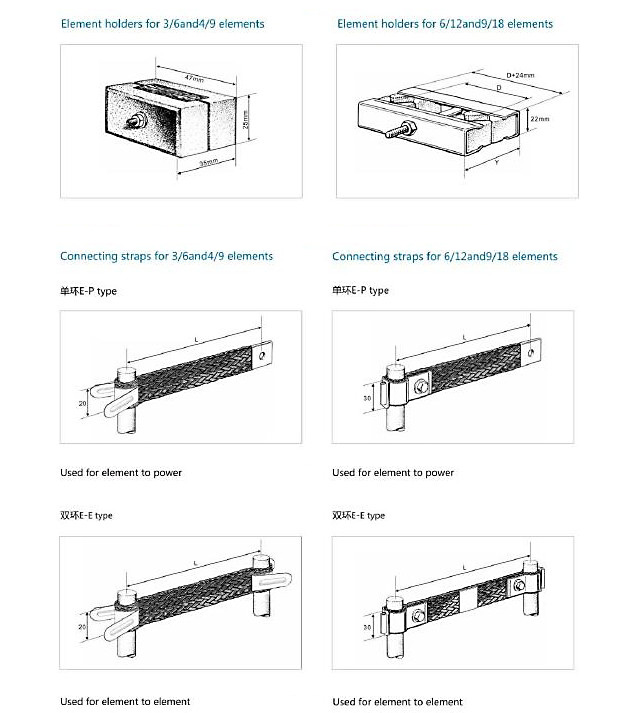
Accessories for elements of different diameters are as follows:
Silicon – molybdenum rod fixing clip – porcelain clip. The role of porcelain clip is to fix silicon-
molybdenum rod to make it hang vertically. Different types of porcelain clip can be selected according to the distance between silicon-molybdenum rods.
The silicon-molybdenum bar weaving clamp has a bright surface, good heat dissipation and good electrical conductivity because the fixing clips of the connecting strip are all screwed up with screws and the coefficient of thermal expansion is small.
Silicon – molybdenum rod aluminum strip clamp, connecting strip is made of high-quality aluminum foilstrip through special process and has good conductivity.
The whole set of single-ring fixture for silicon-molybdenum rod includes two connecting belts and aporcelain fixture. The whole set of double-ring clamps for silicon-molybdenum bars includes a double-ring connecting belt and a porcelain clamp.
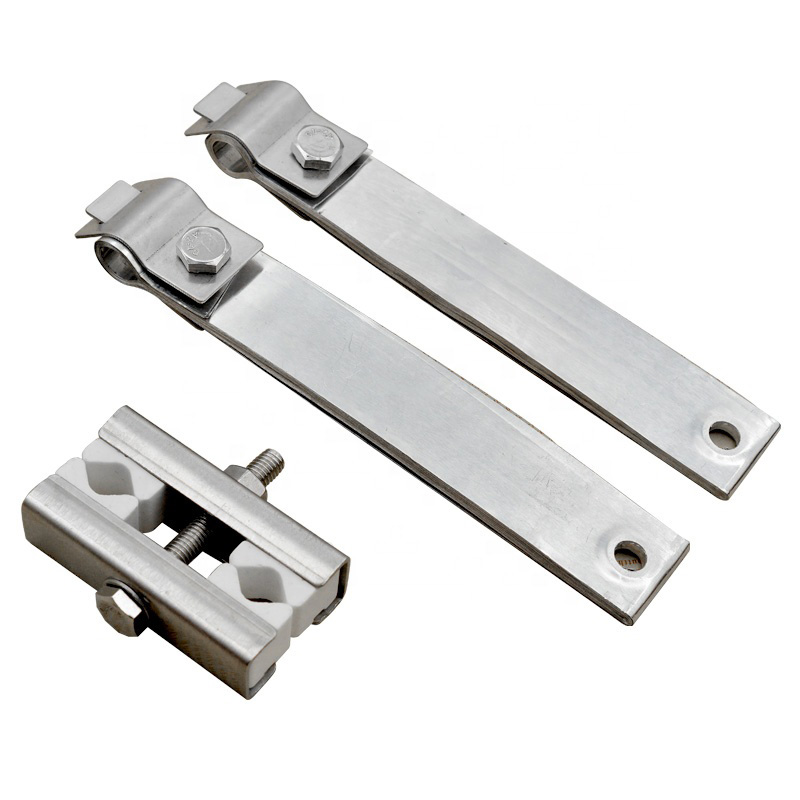
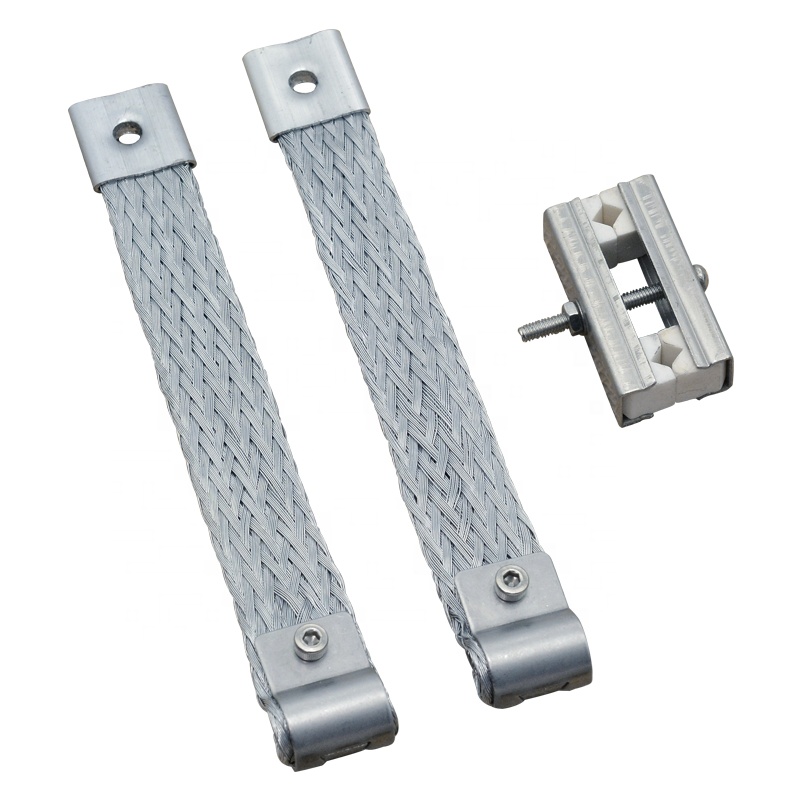
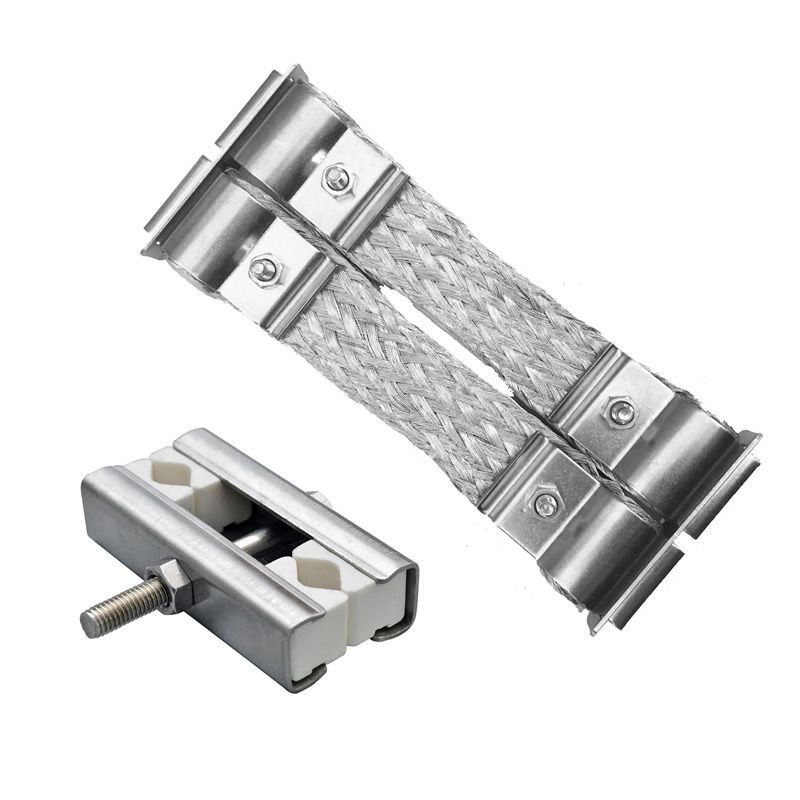



The single ring clamp is used to connect the silicon molybdenum rod element with the power supply. Double ring clamps are used for connection between silicon molybdenum rod elements.
Usage Cautions of MoSi2 Heating Elements
1. MoSi2 heating element is very brittle, which must be installed carefully to prevent breakage.
2. At the beginning of heating, the resistance of MoSi2 heating element is very small. Please offer 1/3 voltage initially to avoid breakage due to big current shock. The voltage should be increased according to rising temperature.
3. MoSi2 heating element can’t be used for a long time in the temperature range of 400 ℃ to 700 ℃, otherwise it will be strongly oxidated and damaged.
4. MoSi2 heating element can get a long lifetime if working in an oxidizing atmosphere such as air, oxygen or carbon dioxide. Reducing gas and corrosive gas will seriously affect the using life.
5. The resistance of MOSi2 heating element does not vary with the length of using time, so the old and new products can be mixed.
6. The conical part of MoSi2 heating element must deep into furnace chamber.
7. The working current of ¢6mm heating element can’t exceed 170A for a long time. The working current of ¢9mm heating element can’t exceed 300A for a long time.
8. The distance between two heating elements in the furnace should be more than the distance of center-to-center in one element.
Operation of MoSi2 Furnace
Drying of The Furnace
Newly built or long-term unused stoves need to be dried before use. Generally, the drying temperature is 100 – 200 ℃, while the long-term use of components at low temperatures will cause low-temperature oxidation.
The drying time of the small furnace is short, and a few hours have little influence on the components. The drying time of large furnace is long and needs attention. In order to ventilate, it is better to open the oven door, which can be ajar as the temperature rises, and completely close the oven door above 1000 ℃.
Starting of The Furnace
If the furnace is dry or can be started up without drying, the following steps should be taken to avoid overload of electrical equipment due to excessive current impact:
| Small furnace (power<100kw) | Large furnace (power 100-500kw) | ||
| furnace temp | Voltage | furnace temp | Voltage |
| 20-150℃ | 1/3 working voltage | 20-300℃ | 1/3 working voltage |
| 150-500℃ | 2/3 working voltage | 300-700℃ | 2/3 working voltage |
| 500℃ working temp | full working voltage | 700℃ working temp | full working voltage |
Replacing of Element
In case of component damage during operation, the position shall be determined first, and the assembled components shall be prepared at the same time. Then loosen the screw connecting the damaged component clamp lead to the bus bar, clean up the ceramic cotton, pull out the ceramic cotton together with the brick, insert the new combined component from the top of the furnace, connect the lead, and plug up the ceramic cotton to raise the temperature.
How to Replace Mosi2 Heating Element
1. Take of 4 screws on top of furnace, and then open the cover, as Fig 01
2. Take off the screw of clip for heating element, as Fig 02
3. Take off aluminum plates between connections of heating element, as Fig 03



4. Take off the screws of metal clip for fixing ceramic block, as Fig 04
5. Take off the ceramic black between rods of U type heating element, as Fig 05
6. Take off the U type heating element which needs to be replaced, as Fig 06
7. Replace a new heating element. Please put ceramic block together with the heating element, and make sure the ceramic block shall fit position as before, as Fig 07




8. When tighten the screw of metal clip for heating element, please make sure the bottom of U heating element does not touch the bottom of furnace chamber. Usually the bottom of U element shall rise 5 mm high from the bottom of furnace chamber.
9. Then, follow the procedure 4, 3, 2, 1 to tighten screw and finish the exchange of heating element.








