Table of Contents
Overview
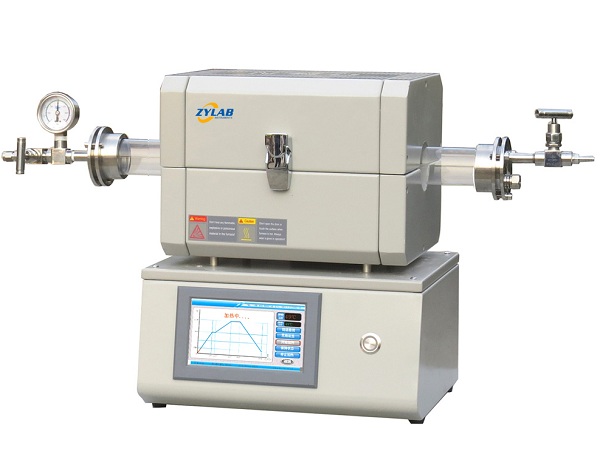
A mini tube furnace is a compact and versatile high-temperature heating device commonly used in laboratories and small-scale industrial settings. It is designed for applications that require controlled and high-temperature environments in a compact form factor.
Mini tube furnaces are well-suited for research, sample preparation, materials processing, and a variety of high-temperature processes.
Features
Compact Design: Mini tube furnaces have a small footprint and are ideal for limited laboratory or bench space.
High-Temperature Capability: They can reach temperatures typically exceeding 1000°C, depending on the model.
Precise Temperature Control: These furnaces offer accurate temperature control through integrated controllers or software.
Uniform Heating: The design ensures even temperature distribution along the length of the tube.
Safety Features: Many models come with safety features such as over-temperature protection and interlocks.
Portability: Their compact size and lightweight construction make mini tube furnaces relatively portable.
Work Process
1. Samples or materials are loaded into a tube or container within the mini tube furnace.
2. The heating elements are activated, and the temperature is gradually raised to the desired level.
3. The materials undergo the required processes with precise temperature control and uniform heating.
4. After the process is complete, the furnace is allowed to cool down before samples are removed.
Applications
Materials Processing: Used for sintering, annealing, and heat treatment of small quantities of ceramics, metals, and semiconductors.
Chemical Reactions: Facilitates processes like chemical vapor deposition (CVD), thermal decomposition, and materials synthesis.
Materials Research: Employed for materials characterization, crystal growth, and catalyst testing.
Sample Preparation: Suitable for ashing, drying, and pre-processing of small samples for analytical techniques.
Benefits
1. Space-saving design for laboratories with limited space.
2. Precise temperature control for consistent results.
3. Uniform heating along the length of the tube.
4. Portable and adaptable for various laboratory applications.
Price
The price of a mini tube furnace can vary depending on factors such as temperature range, tube material, size, and additional features.
Basic models may start at a few thousand dollars, while more advanced models can cost several thousand dollars.
Considerations When Purchasing
Temperature Range: Ensure the furnace can achieve the required temperature for your specific applications.
Tube Material: Select the appropriate tube material (e.g., alumina, quartz, or ceramic) based on sample compatibility.
Temperature Control System: Evaluate the precision and ease of use of the temperature control system.
Safety Features: Consider safety features like over-temperature protection and emergency shut-off systems.
Size and Capacity: Choose a model that can accommodate your sample size and quantity.
Atmosphere Control: Determine if you need the furnace to operate in a controlled atmosphere, such as inert gas or vacuum.
Supplier Reputation: Research and select a reputable supplier with professional knowledge.
FAQ
1. Can I use a mini tube furnace for controlled atmosphere experiments?
Some models can be equipped with controlled atmosphere capabilities, such as inert gas or vacuum.
2. What maintenance is required for a mini tube furnace?
Regular cleaning and inspection are necessary. Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for maintenance procedures.
3. Can I observe the sample inside the mini tube furnace during heating?
Observation is typically not possible, as most tube materials are not transparent. Some models with quartz tube are available.
4. What’s the difference between a mini tube furnace and a standard tube furnace?
The main difference is size and capacity.
Mini tube furnaces are designed for smaller sample sizes and limited laboratory space, while standard tube furnaces are larger and can handle larger quantities of materials.
The choice depends on the specific application and space constraints.