Table of Contents
What is Powder?
Powder refers to materials that exist in a fine particulate state under normal conditions.
Specifically, powder is an aggregate composed of a large number of solid particles and the gaps between them. Examples include flour, soy milk powder, milk powder, coffee powder, rice flour, wheat flour, soybean powder, and salt in food; sand, soil, dust, and sandstorms in nature; and industrial products like gunpowder, cement, pigments, medicines, and fertilizers. These materials all belong to the category of powders.

Their common characteristics are a large specific surface area, composed of substances in particulate form with varying sizes, and gaps between the particles.
What is Powder Processing?
Powder processing refers to the process of treating solid raw materials into powder form or further processing powders.
It involves multiple steps and techniques, including ultrafine grinding, precision grading, high homogenization, dispersion, composite coating, modification, drying, sintering, storage, packaging, and transportation, aiming to improve powder performance, enhance production efficiency, and meet specific industrial demands.
Powder Processing Techniques:
Conveying, Storage, and Feeding
Purpose: To transfer powder materials from one processing stage to another while maintaining their flowability and stability during processing.
Equipment: Silos, vibrating feeders, screw feeders, etc.
Crushing
Purpose: To grind larger particles or lumps into finer powder to increase the material’s specific surface area and reactive activity.
Equipment: Ball mills, pin mills, jet mills, etc.
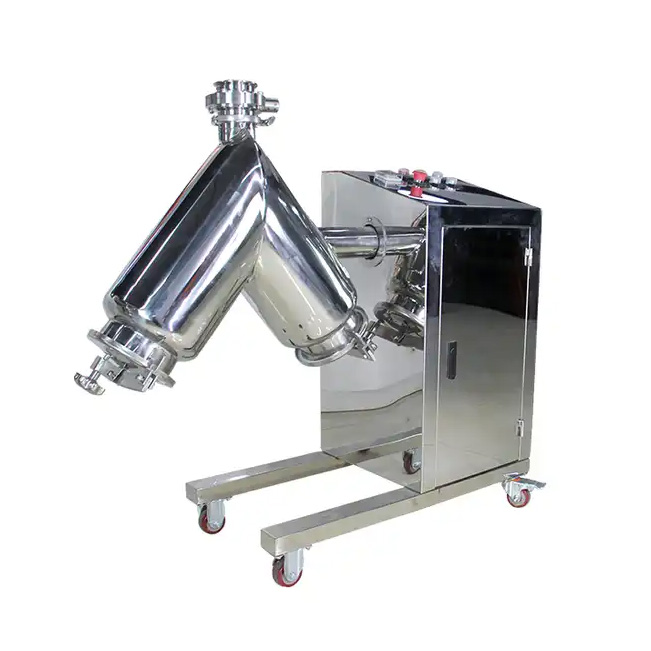
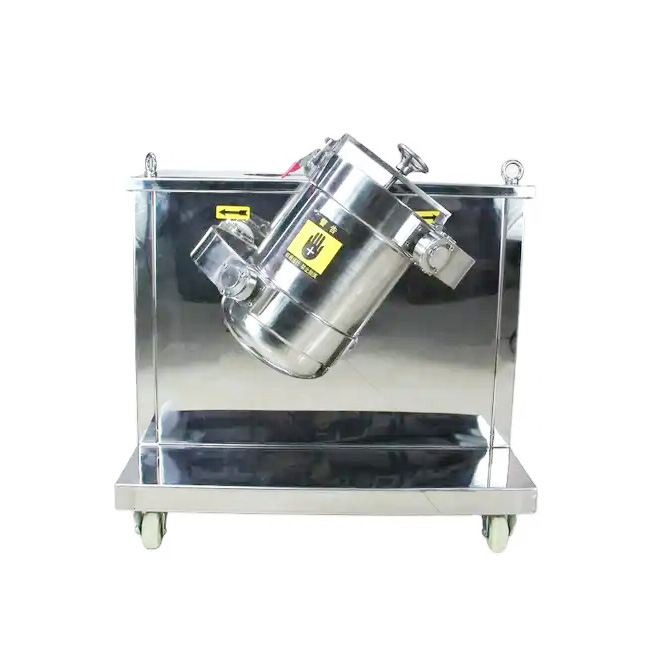
Mixing
Purpose: To evenly blend powders of different components to ensure consistency in the composition and performance of the final product.
Methods: Container rotation mixing, forced stirring mixing.
Drying
Purpose: To remove moisture or other volatile substances from the powder to prevent caking or performance changes in subsequent processes.
Methods: Airflow drying, spray drying.
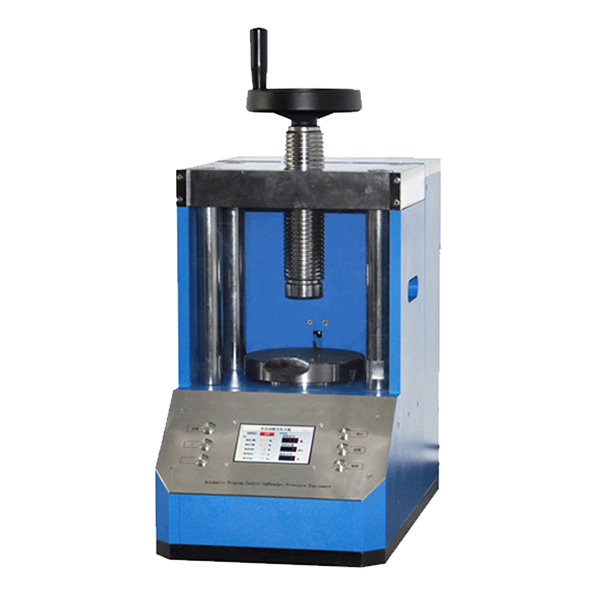
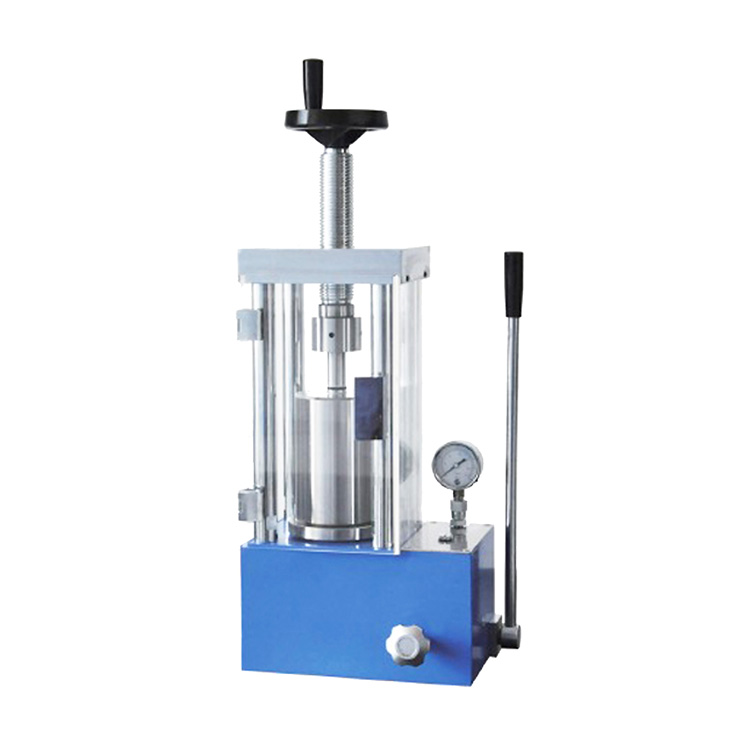
Granulation and Forming
Purpose: To convert fine powders into larger granules or solid products of specific shapes to improve handling and product performance.
Methods: Rotating stirring granulation, extrusion forming.
Classification and Separation
Purpose: To classify or separate powder materials based on particle size or density to obtain powder with the desired specifications.
Methods: Air classification, vibrating screening, gravity separation.
Dust Collection
Purpose: To collect dust generated during production, reducing material loss and protecting the environment and workers’ health.
Equipment: Collectors, cyclone separators, etc.
Ultrasonic Treatment
Purpose: To use ultrasonic energy to disperse, deagglomerate powders, or improve their flowability and distribution uniformity.
Applications: Nano-powder, ultrafine powder processing, etc.
Applications:
Chemical Industry
Catalysts: By precisely controlling powder particle size and surface characteristics, high-efficiency catalysts are prepared for use in petrochemical and fertilizer production.
Pigments and Coatings: Pigments are ground into ultrafine powders to enhance the coverage and color uniformity of coatings.
Plastic Additives: Powder processing is used to prepare plasticizers, fillers, and flame retardants to enhance plastic performance.
Pharmaceutical Industry
Drug Formulations: Powder processing (such as crushing, mixing, and granulation) is used to prepare tablets, capsules, oral powders, etc., ensuring uniformity and bioavailability of the drugs.
Drug Nanotechnology: Ultrafine grinding techniques are used to produce nanoscale drug particles, improving solubility and absorption rates.
Food Industry
Powdered Food Additives: Production of additives such as flour improvers, seasonings, and vitamin powders to improve food texture, extend shelf life, or increase nutritional value.
Beverage Powders: Spray drying and mixing techniques are used to produce instant coffee, milk powder, protein powder, etc., ensuring solubility and taste.
Building Materials and Ceramics Industry
Cement Production: Limestone and clay are crushed into fine powder and then sintered and ground to produce cement for construction projects.
Ceramic Powders: Crushing and mixing are used to prepare ceramic materials for tiles, pottery, electronic ceramics, etc.
Glass Powder: Used in glass manufacturing and fiberglass production, requiring strict control over powder purity and particle size distribution.
Metal Powder Metallurgy
Metal Component Manufacturing: Powder metallurgy techniques are used to produce metal components for automotive, aerospace, and electronics, achieving complex shapes and high precision.
3D Printing Materials: Metal powders are used in 3D printing through powder bed fusion or binder jetting to create precise parts and prototypes.
Energy Industry
Lithium Battery Materials: Powder processing is used to prepare high-performance anode and cathode materials, such as lithium cobalt oxide and graphite, to enhance battery capacity and stability.
Fuel Cell Powders: Production of catalysts and electrode materials for fuel cells, such as platinum-based catalysts and lithium titanate, to improve efficiency and lifespan.
Environmental Industry
Water Treatment Materials: Preparation of activated carbon powder, nano-alumina, etc., for water purification, pollutant adsorption, and wastewater treatment.

Air Purification Materials: Powder processing produces activated carbon and catalysts for air filters to remove harmful substances from the air.
Waste Treatment Catalysts: Production of catalysts for waste incineration or industrial waste gas treatment, reducing pollutant emissions.
Electronic Materials
Semiconductor Powders: Used in the manufacturing of electronic components, such as silicon dioxide and gallium nitride powders, requiring extremely high purity and uniformity.
Magnetic Materials: Powder metallurgy processes are used to produce high-performance magnetic materials for motors, transformers, sensors, etc.
Aerospace
Lightweight Alloy Powders: Used to manufacture lightweight, high-strength components for aircraft and spacecraft, such as titanium and aluminum alloy powders.
High-Temperature Materials: Powder processing is used to prepare high-temperature coatings and components for use in aerospace engines and spacecraft surface protection.
Cosmetics Industry
Powdered Cosmetics: Powder processing is used to produce loose powder, eyeshadow, blush, and other cosmetics, requiring a fine texture and good adhesion.
Nanotechnology of Active Ingredients: Active ingredient powders are nanonized to enhance absorption and effectiveness in cosmetics.
Powder-Related Industries and Processing Steps:
Coal & Mining
Crushing – Grading – Conveying
Food
Storage – Crushing – Grading – Mixing – Sterilization – Dissolution – Crystallization
Paper & Pulp
Mixing – Filtration – Drying
Rubber & Polymers
Crushing – Grading – Mixing – Filtration
Pigments & Fillers
Crushing – Grading – Mixing – Crystallization – Filtration – Drying
Chemical Industry
Crushing – Dissolution – Crystallization – Filtration – Drying
Steel
Crushing – Grading – Mixing – Granulation – Sintering
Electronic Materials
Crushing – Mixing – Forming – Sintering
Pharmaceuticals
Mixing – Forming – Crushing – Grading – Mixing – Granulation – Forming
Battery Materials
Mixing – Sintering – Crushing – Grading – Mixing – Magnetic Separation