Table of Contents
Overview
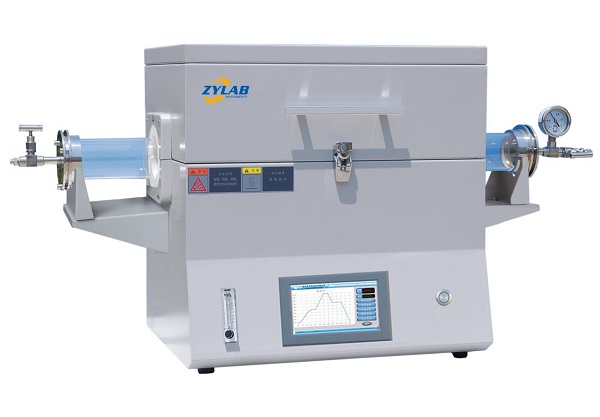
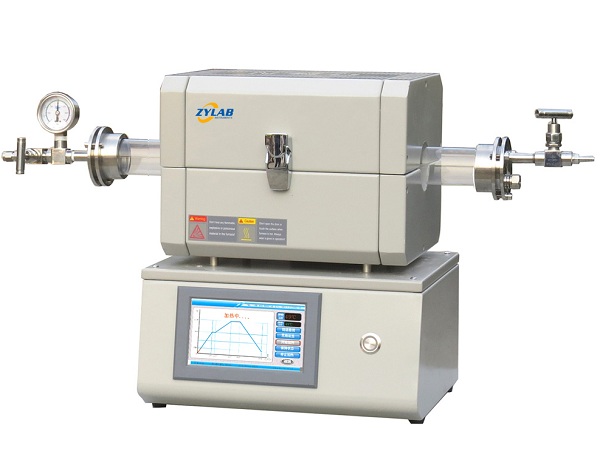
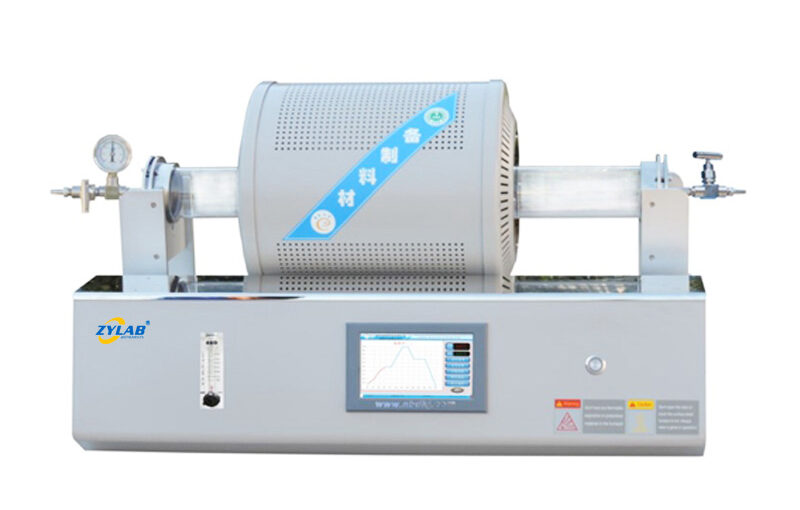
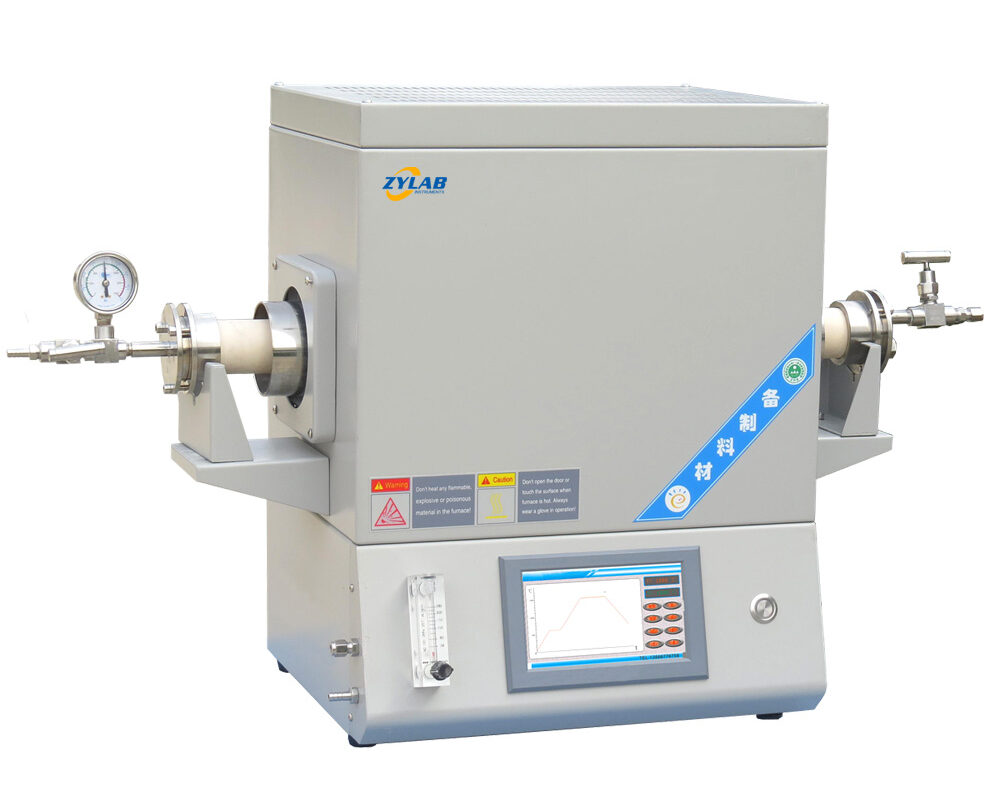
A laboratory tube furnace is a specialized heating device used in research and industrial laboratories for high-temperature applications. It consists of a cylindrical heating chamber, typically made of refractory materials, and an integrated heating element.
A laboratory tube furnace is comprises a tubular chamber where samples or materials are heated to high temperatures for processes such as annealing, sintering, chemical reactions, and materials research.
Features
High-Temperature Capability: Tube furnaces can reach temperatures ranging from a few hundred degrees Celsius to over 1,000°C, depending on the model.
Precise Temperature Control: They offer accurate temperature control through integrated controllers or software.
Uniform Heating: These furnaces provide even temperature distribution along the length of the heating chamber.
Versatility: Tube furnaces are adaptable for different applications by using different tube materials and atmosphere control options.
Work Process
Applications
Chemical Reactions: They facilitate chemical vapor deposition (CVD), thermal decomposition, and other chemical processes.
Materials Research: Widely employed for materials characterization, crystal growth, and catalyst testing.
Sample Preparation: Used for ashing, drying, and pre-processing of samples for analytical techniques.
Benefits
1. Precise temperature control for consistent results.
2. Versatility in terms of sample types, materials, and atmospheres.
3. Compact and space-efficient for laboratory settings.
4. Can be equipped with various accessories for specific applications.
Price
The price of a laboratory tube furnace can vary widely based on factors such as temperature range, tube material, and additional features. Basic models can cost several thousand dollars, while more advanced and larger furnaces can range from tens of thousands to over a hundred thousand dollars.
Considerations When Purchasing
Temperature Range: Ensure the furnace can achieve the required temperature for your specific applications.
Tube Material: Select the appropriate tube material (e.g., quartz, ceramic, metal) based on sample compatibility.
Atmosphere Control: Determine if you need the furnace to operate in a controlled atmosphere, such as inert gas or vacuum.
Safety Features: Consider safety features like over-temperature protection and emergency shut-off systems.
Size and Capacity: Choose a model that can accommodate your sample size and quantity.
Temperature Control System: Evaluate the precision and ease of use of the temperature control system.
FAQ
1. Can I use a laboratory tube furnace for controlled atmosphere experiments?
Yes, many models can be equipped with controlled atmosphere capabilities, such as inert gas or vacuum.
2. Are there tube furnaces with multiple heating zones for complex processes?
Yes, some tube furnaces have multiple heating zones for creating temperature gradients and executing more complex heat treatment processes.
3. What maintenance is required for a tube furnace?
Regular cleaning and inspection are necessary. The manufacturer’s guidelines should be followed for maintenance procedures.
4. Can I observe the sample inside the tube furnace during heating?
Observation is possible if the tube is transparent, such as quartz. However, some models offer viewports for monitoring.
5.What’s the difference between a tube furnace and a muffle furnace?
A tube furnace has a tubular heating chamber, while a muffle furnace is a box-shaped chamber with a heating element surrounding it.