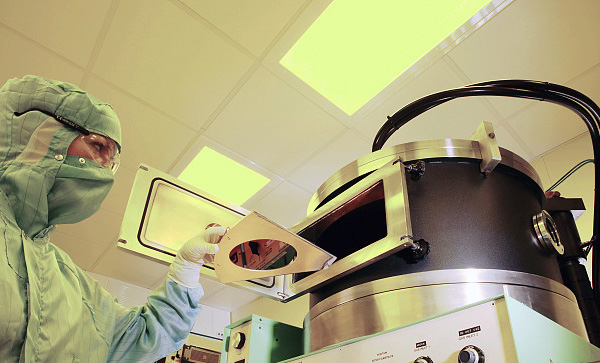
Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition (PECVD) is a widely used thin-film deposition technique in semiconductor manufacturing, optics, photovoltaics, and other advanced material applications. Compared to traditional Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), PECVD offers significant advantages, particularly in achieving high-quality films at lower temperatures.
Category Archives: Thermal Processing
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) technology is widely used in semiconductor manufacturing, optics, thin-film coatings, and material science. Within this technology, different types of CVD furnaces exist, including CVD, PECVD (Plasma-Enhanced CVD), and FBCVD (Fluidized Bed CVD).
Biochar is a high-carbon, porous solid material produced by pyrolyzing biomass under oxygen-limited or inert gas conditions. In laboratories, a muffle furnace (Muffle Furnace) is commonly used for biochar preparation, as it provides a stable high-temperature environment to ensure process control.
Both muffle furnaces and tube furnaces serve essential roles in high-temperature applications, but choosing the right one depends on your specific needs. If you require a chamber-style furnace for bulk materials, a Muffle Furnace is the best choice. However, if you need controlled atmospheres and precise gas flow for your experiments, a Tube Furnace is more suitable.
Vacuum tube furnaces play a critical role in advanced material synthesis, enabling researchers and industry professionals to achieve precise control over temperature, atmosphere, and reaction environments. These furnaces are indispensable in fields such as nanotechnology, energy storage, and semiconductor research.
Box furnaces are essential high-temperature heating equipment used in laboratories, research facilities, and industrial settings. They provide a controlled environment for applications such as heat treatment, sintering, and material testing. Their box-like chamber design allows for uniform temperature distribution, making them ideal for various thermal processing tasks.
Each type offers unique advantages based on heating uniformity, material processing capabilities, and specific research or production requirements. In this article, we compare these three types of furnaces to help you determine which one best suits your needs.
By carefully controlling temperature, heating duration, and cooling methods, materials can achieve enhanced hardness, strength, and corrosion resistance. Using ZYLAB high-temperature furnaces, researchers and engineers can optimize heat treatment processes for superior material performance.
Unlike conventional furnaces, RTA furnaces minimize thermal exposure, preventing undesirable diffusion effects while preserving material integrity. These furnaces operate at temperatures ranging from 200°C to over 1200°C, depending on the specific application.
Muffle furnaces are widely used for processes such as soil testing, biochar production, and thermal analysis, providing researchers with precise temperature control, reliable performance, and uniform heating for consistent experimental results.