Table of Contents
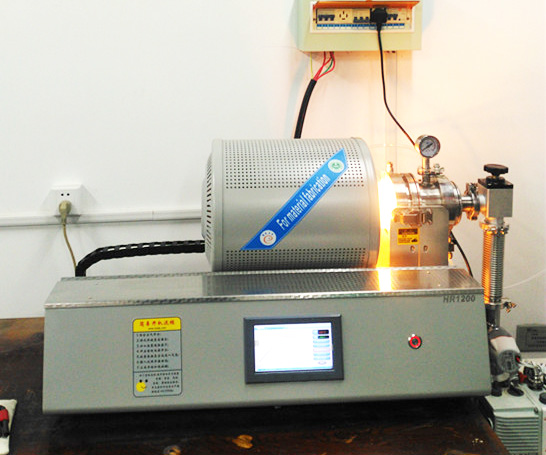
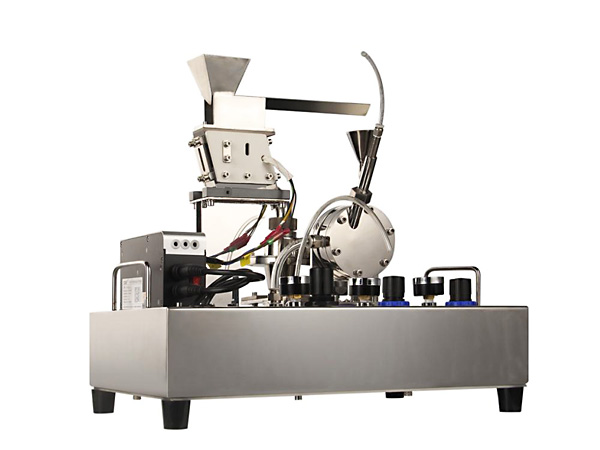
Box furnaces, also known as chamber furnaces or rectangular furnaces, are versatile pieces of equipment used in a wide range of industrial, research, and manufacturing applications. Their enclosed design allows for controlled heating, temperature uniformity, and often the ability to introduce controlled atmospheres.
Applications
Here are some common applications of box furnaces:
1. Heat Treatment:
Box furnaces are extensively used for heat treatment processes such as annealing, tempering, hardening, and quenching of metals and alloys. These processes can modify the mechanical properties, hardness, and microstructure of materials.
2. Sintering:
Box furnaces are utilized in sintering operations, where powdered materials are heated to a temperature below their melting point to achieve bonding and densification. This process is widely employed in ceramics, powder metallurgy, and advanced material manufacturing.
3. Brazing and Welding:
Box furnaces can be used for controlled atmosphere brazing and welding, ensuring strong and reliable joints in applications like aerospace, automotive, and electronics.
4. Glass Annealing:
The controlled temperature environment of a box furnace is crucial for annealing glass products, reducing internal stresses and improving the overall strength and quality of the glass.
5. Ceramic Firing:
Box furnaces are used to fire ceramics and pottery at specific temperatures, allowing them to achieve the desired properties and aesthetics.
6. Research and Development:
Box furnaces are essential tools in materials research, allowing scientists to study the effects of different heat treatments on various materials and to develop new materials with specific properties.
7. Crystal Growth:
For research and manufacturing purposes, box furnaces are employed in crystal growth processes, including the production of semiconductor crystals and single crystals for research and industrial applications.
8. Thermal Testing:
Box furnaces are used for thermal testing, including thermal expansion measurements, thermal conductivity tests, and other studies involving changes in materials’ properties with temperature.
9. Pyrolysis and Carbonization:
In the production of carbon materials, like carbon fibers and carbon composites, box furnaces can be used for pyrolysis and carbonization processes, which involve controlled heating of precursor materials.
10. Drying and Curing:
Box furnaces are used in the drying and curing of coatings, paints, adhesives, and other materials where controlled temperature and heating profiles are essential for proper curing.
11. Aging and Stress Relief:
Box furnaces are used for stress relief annealing, which helps to reduce residual stresses in metals and other materials, thereby enhancing their stability and performance.
12. Educational and Training:
Box furnaces are valuable tools in educational institutions for teaching heat treatment processes, material behavior, and laboratory techniques.
13. Quality Control:
Industries use box furnaces for quality control purposes, ensuring that products meet specific heat treatment requirements and maintaining consistent material properties.
14. Aerospace and Defense:
Box furnaces play a role in the aerospace and defense sectors for processes like diffusion bonding, thermal barrier coatings, and production of components for engines and propulsion systems.
15. Jewelry and Artwork:
In jewelry-making and artistic applications, box furnaces are used for tasks such as enameling, glass fusing, and precious metal work.
Conclusions
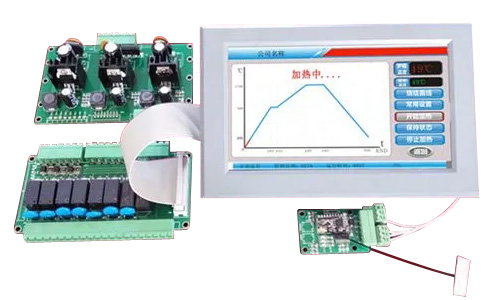
Box furnaces can be customized with various features, including different heating elements, temperature controls, programmable controllers, gas injection systems, and more, to suit the specific needs of different applications.
Benefits
Box furnaces offer a range of benefits that make them valuable tools in various industrial, research, and manufacturing settings.
Here are some of the key benefits of using box furnaces:
1. Temperature Control:
Box furnaces provide precise temperature control, allowing users to achieve and maintain specific temperature profiles critical for various heat treatment and material processing operations.
2. Uniform Heating:
These furnaces are designed to ensure uniform heat distribution within the chamber, resulting in consistent processing and material properties throughout the load.
3. Versatility:
Box furnaces can be used for a wide range of applications, from heat treatment and annealing to sintering, brazing, and more, making them versatile tools for different industries and processes.
4. Controlled Atmospheres:
Many box furnaces can operate in controlled atmospheres, including inert gases, reducing gases, or even partial vacuums. This is crucial for processes that require specific gas environments to prevent oxidation or achieve specific reactions.
5. Enclosed Design:
The enclosed chamber design of box furnaces helps prevent heat loss to the surrounding environment, ensuring energy efficiency and faster heating and cooling rates.
6. Customization:
Manufacturers often offer customization options for box furnaces, allowing users to tailor the furnace’s features, size, and controls to meet specific application requirements.
7. High-Temperature Capability:
Many box furnaces can achieve high temperatures, making them suitable for applications that require extreme heat, such as ceramics, advanced materials, and metalworking.
8. Batch Processing:
Box furnaces are well-suited for batch processing, allowing multiple parts or samples to be processed simultaneously, which can increase productivity and efficiency.
9. Quality Assurance:
Box furnaces are essential for achieving consistent material properties and quality in heat-treated or processed materials, making them valuable in industries where product reliability is critical.
10. Research and Development:
Researchers and scientists benefit from box furnaces’ controlled environment, allowing them to study the effects of heat treatment on materials and develop new materials with desired properties.
11. Compact Design:
Box furnaces are available in various sizes, including benchtop models, which is advantageous when space is limited, such as in laboratories or smaller manufacturing facilities.
12. Education and Training:
Box furnaces serve as valuable educational tools, allowing students to learn about heat treatment processes, material behavior, and laboratory techniques in a hands-on manner.
13. Safe Operation:
Modern box furnaces come equipped with safety features such as overtemperature protection, alarm systems, and safety interlocks to prevent accidents and ensure operator safety.
14. Ease of Use:
Many box furnaces are designed with user-friendly interfaces and programmable controls, simplifying their operation and reducing the learning curve.
15. Reliability:
Well-designed box furnaces are built to withstand high temperatures and extended use, providing long-term reliability and consistent performance.
16. Customizable Heating Profiles:
Programmable controllers in box furnaces allow users to create and store complex heating and cooling profiles, enabling precise control over thermal processing cycles.
17. Cost-Effective:
While box furnaces vary in cost depending on features and specifications, they are often more cost-effective than large industrial furnaces, making them suitable for smaller-scale operations.
Conclusions
Overall, box furnaces play a critical role in various industries by enabling precise thermal processing and controlled environments for a wide range of materials and application