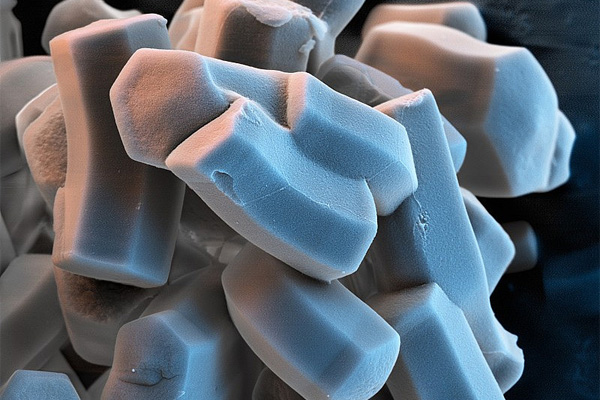
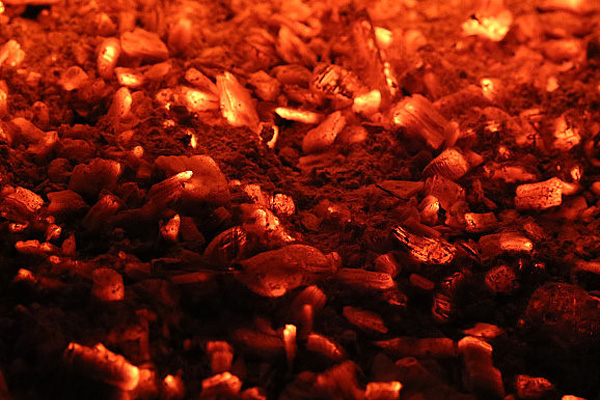
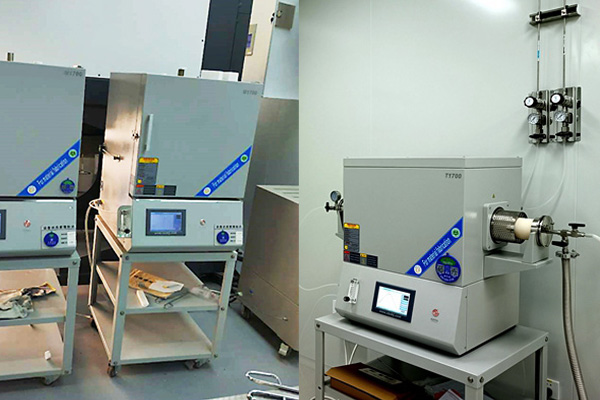
Understanding the Sintering Process of Porous Materials: From Laboratory to Industrial Applications
From laboratory-scale research to large-scale industrial production, selecting the right sintering method is essential for optimizing material performance.