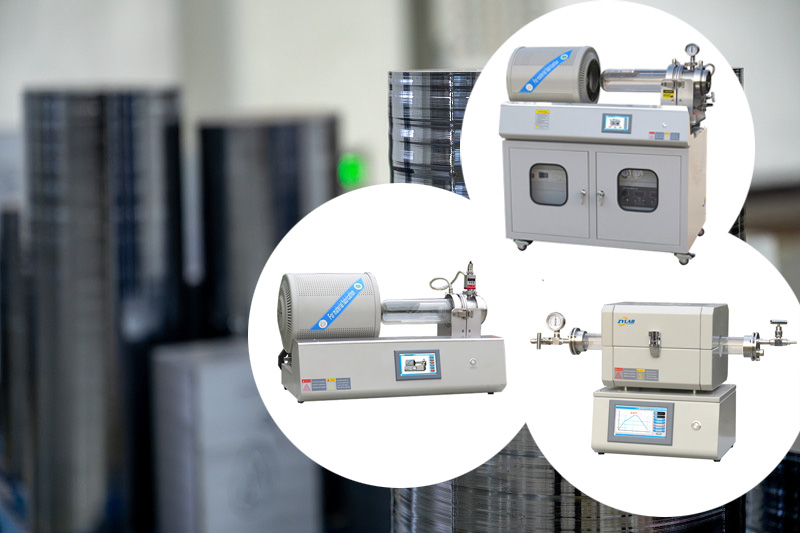
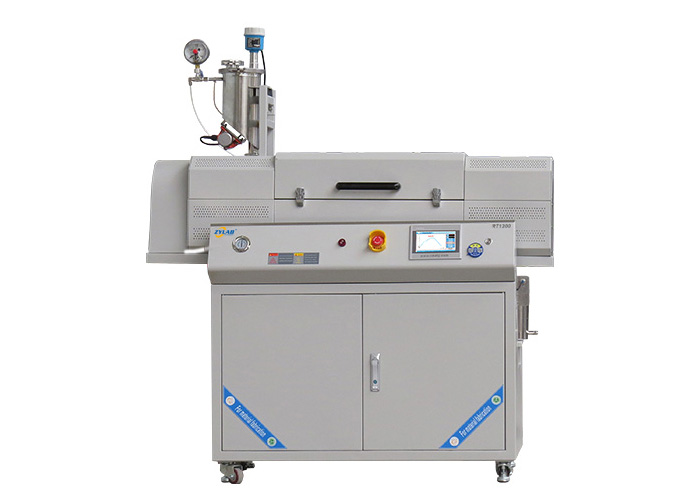
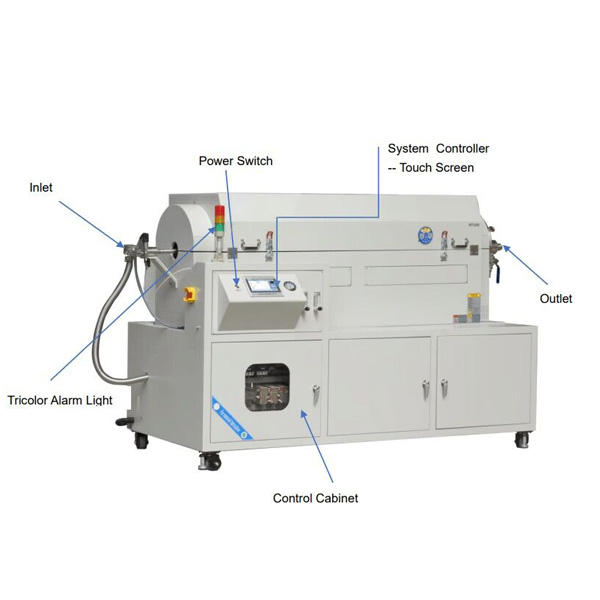
Electric furnaces are a key heating equipment in a wide range of industries, from metallurgy and ceramics to semiconductor manufacturing and advanced materials research.
In this blog, we will explore the applications of electric furnaces in laboratory settings and their role in advancing research and development in various fields.
Material Science and Engineering
Material Science:
In material science, electric furnaces are used for the synthesis and processing of various materials such as ceramics, metals, and composites.
They are used for sintering, annealing, and heat treatment of materials to modify their properties, such as density, porosity, and strength.


Electric furnaces can also be used to melt and cast metals, which is important in the production of alloys and other metallic materials.
Annealing, which involves heating a material to a specific temperature and then cooling it slowly, is another important application of electric furnaces in materials science.
Engineering:
In engineering, electric furnaces are used for the testing of materials and components under high-temperature conditions. These furnaces are used for the evaluation of the performance of materials and components under extreme conditions, such as high-temperature corrosion and wear.
Chemical Research and Analysis
Chemistry research:
electric furnaces are used for high-temperature reactions, such as calcination, pyrolysis, and oxidation. These furnaces are used for the synthesis of various materials, such as nanoparticles and catalysts, and for the purification of chemicals.
Chemical analysis:
electric furnaces are used for thermal analysis techniques, such as differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) and thermogravimetric analysis (TGA), which can provide valuable information about the properties of compounds and materials.
Electric furnaces can also be used for x-ray diffraction (XRD) and x-ray fluorescence (XRF) analysis, which are common methods for identifying the composition and crystal structure of materials.
Environmental Science
Electric furnaces can be used in environmental science research to study the behavior of materials and compounds under high-temperature conditions, such as those found in volcanic environments.

For example, electric furnaces can be used to simulate volcanic gas conditions, which can help to understand the formation of minerals and the behavior of gases in volcanic environments.
Electric furnaces can also be used to study the behavior of pollutants and hazardous materials under high-temperature conditions, which is important for developing methods for their safe disposal and treatment.
Geological and Mineralogical Research

Laboratory electric furnaces are widely used in the geological and mineralogical research field for preparing molten rocks, thermal treatment, and sintering of rocks and minerals.
Electronics and Semiconductors
Electric furnaces are critical in the manufacturing of electronic and semiconductor components. Electric furnaces are used for the deposition and annealing of thin films, which are used in the production of transistors, microchips, and other electronic components.
Electric furnaces can also be used to study the behavior of semiconductors under high-temperature conditions. This is important for understanding the properties of these materials and for developing new materials with specific properties.
Pharmaceutical Research
Electric furnaces are also used in pharmaceutical research for the synthesis and analysis of drug compounds. High-temperature reactions can be used to produce new compounds with specific properties, and electric furnaces can be used to study the behavior of these compounds under different conditions.
Electric furnaces are also used for the analysis of pharmaceuticals and drug compounds using techniques such as XRD and TGA.
Glass and Ceramics Manufacturing

Laboratory electric furnaces are extensively used in the manufacturing of glass and ceramics, including melting, shaping, sintering, and heat treatment processes.
Overall, electric furnaces are essential device in laboratory settings across a wide range of industries, including materials science and engineering, chemistry, environmental science, electronics and semiconductors, and pharmaceutical research.
With their ability to create high-temperature environments, electric furnaces play a critical role in advancing research and development in various fields.