Table of Contents
Introduction
Metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) are highly porous materials with wide-ranging applications in gas storage, catalysis, and separation.
Among the various synthesis methods, solvothermal synthesis is one of the most effective techniques for obtaining high-purity MOF powders with controlled morphology and crystallinity.
This article provides a detailed guide on the solvothermal synthesis process, the required reaction equipment, and key parameters such as temperature and reaction time.
Solvothermal Synthesis Process of MOF Powders
The solvothermal method involves dissolving metal precursors and organic ligands in a suitable organic solvent under high-temperature and high-pressure conditions inside a sealed reaction vessel. The step-by-step process is as follows:
1. Preparation of Precursors
- Dissolve a metal salt (e.g., Zn(NO₃)₂, Cu(NO₃)₂, FeCl₃) and an organic linker (e.g., terephthalic acid, trimesic acid, imidazolate) in a polar organic solvent such as N,N-Dimethylformamide (DMF), ethanol, or acetonitrile.
- Adjust the solution pH using acidic or basic additives if needed.
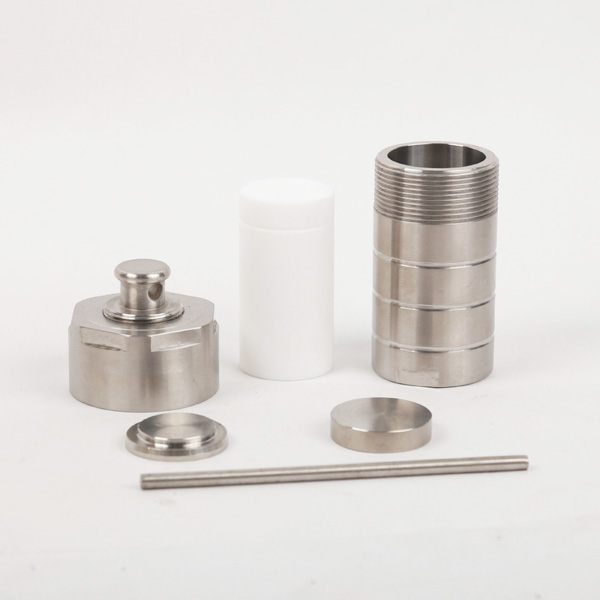
2. Transfer to a Sealed Reaction Vessel
- The prepared precursor solution is poured into a high-pressure reactor, typically a Teflon-lined stainless steel autoclave or a glass-lined hydrothermal reactor.
- The vessel is securely sealed to maintain high-pressure conditions during heating.

3. Solvothermal Reaction
- The sealed reactor is placed inside a laboratory oven or a heating mantle for controlled temperature treatment.
- The reaction temperature generally ranges from 100°C to 250°C, depending on the specific MOF being synthesized.
- The reaction time varies from 12 to 48 hours, allowing sufficient crystal growth.
4. Cooling and Filtration
- After the reaction is complete, the autoclave is cooled to room temperature naturally or by water cooling to avoid thermal stress.
- The obtained MOF crystals are separated by vacuum filtration or centrifugation, followed by thorough washing with fresh organic solvent to remove residual unreacted precursors.
5. Drying and Activation
- The purified MOF powder is dried under vacuum or in an oven at 60-120°C to remove residual solvent.
- For enhanced porosity, MOFs may undergo solvent exchange with a low-surface-tension liquid like methanol, followed by activation under vacuum at 150-250°C to remove trapped solvents from the pores.
Key Equipment for MOF Solvothermal Synthesis
1. High-Pressure Autoclave (Teflon or Glass-Lined)
- Essential for maintaining high-temperature and high-pressure reaction conditions.
- Available in various sizes for small-scale lab research or pilot-scale synthesis.
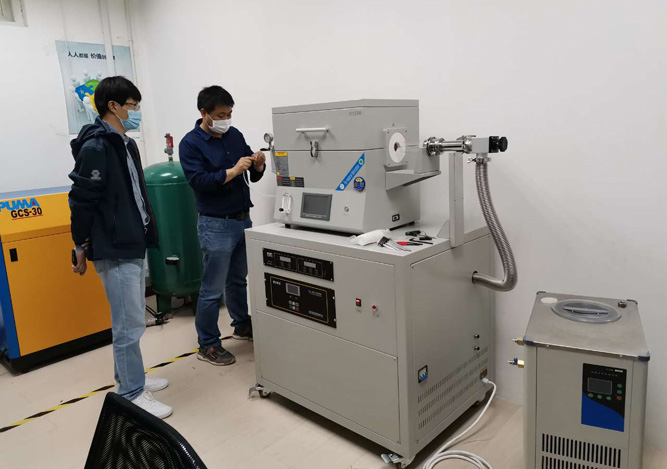
2. Temperature-Controlled Oven or Heating Mantle
- Provides precise heating to ensure uniform temperature distribution.
- Some models allow programmable temperature ramping for optimized synthesis conditions.
3. Vacuum Filtration System
- Used for efficient separation and purification of MOF crystals.
- Includes a vacuum pump, filter flask, and membrane filter.
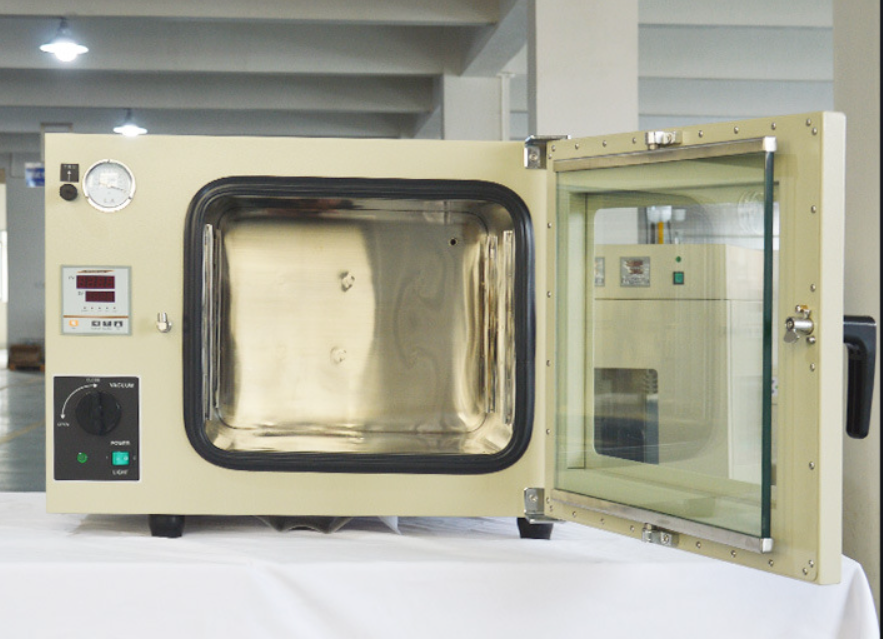
4. Vacuum Drying Oven
- Ensures complete removal of residual solvents while maintaining the MOF’s porous structure.
Optimal Reaction Conditions for MOF Synthesis
| Parameter | Typical Range | Importance |
| Temperature | 100°C – 250°C | Affects crystal growth and porosity |
| Pressure | 10 – 50 bar | Maintains solvent in liquid phase at high temperature |
| Reaction Time | 12 – 48 hours | Longer time leads to better crystallinity |
| Solvent | DMF, ethanol, water | Determines solubility and crystal formation |
| pH Control | 4 – 9 (varies by MOF) | Optimizes nucleation and growth |
Conclusion
Solvothermal synthesis is a highly effective method for producing MOF powders with well-defined morphology and high porosity. By carefully selecting the reaction temperature, time, solvent, and equipment, researchers can optimize MOF crystallinity and performance.
ZYLAB provides advanced high-pressure reactors and temperature-controlled heating systems for laboratory MOF production. Contact us today to learn more about our specialized equipment solutions!





