Table of Contents
Annealing furnaces and sintering furnaces are commonly used equipment in the heat treatment process, playing important roles in material processing and modification.
Functional Differences
Annealing is a heat treatment process that involves heating materials to a certain temperature and then controlling the cooling rate to alter the material’s crystal structure, relieve internal stress, enhance toughness and ductility, and improve its mechanical properties.
During annealing, dislocations and stresses in the lattice are released, and grains undergo recrystallization, thereby increasing the material’s plasticity, reducing hardness, and improving machinability and corrosion resistance.
Sintering is also a heat treatment process that involves heating powder or granular materials to temperatures close to their melting points, followed by controlled cooling in a controlled atmosphere to induce diffusion, solidification, and bonding between particles, thus forming denser bulk objects.
Sintering furnaces provide the necessary temperature and atmosphere control during this process to facilitate bonding between particles and achieve the desired physical and chemical properties.
Structural Differences
Both annealing furnaces and sintering furnaces typically consist of a heating chamber and a temperature control system, with some models equipped with a protective atmosphere system to provide inert gases such as nitrogen or argon.
Some annealing furnaces are equipped with a cooling control system to achieve precise control of the material’s cooling rate.
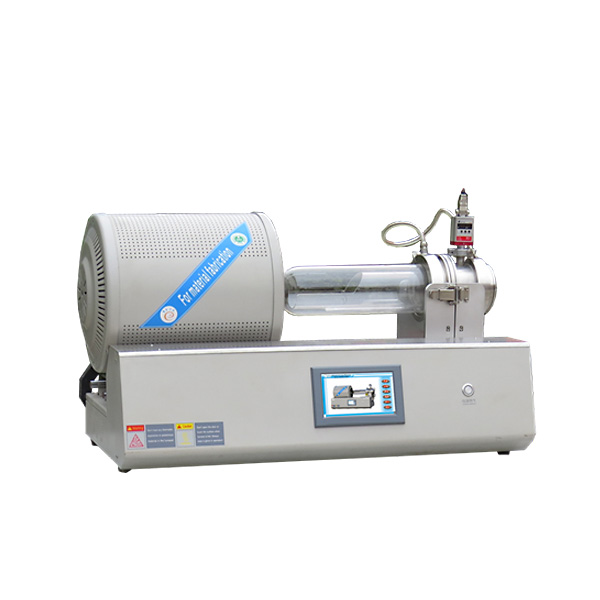
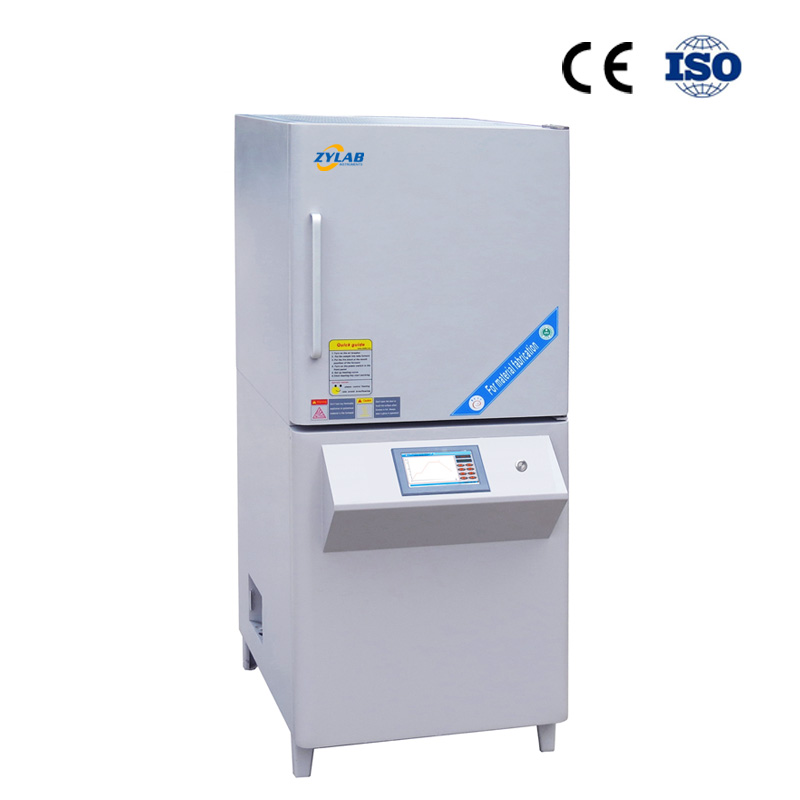
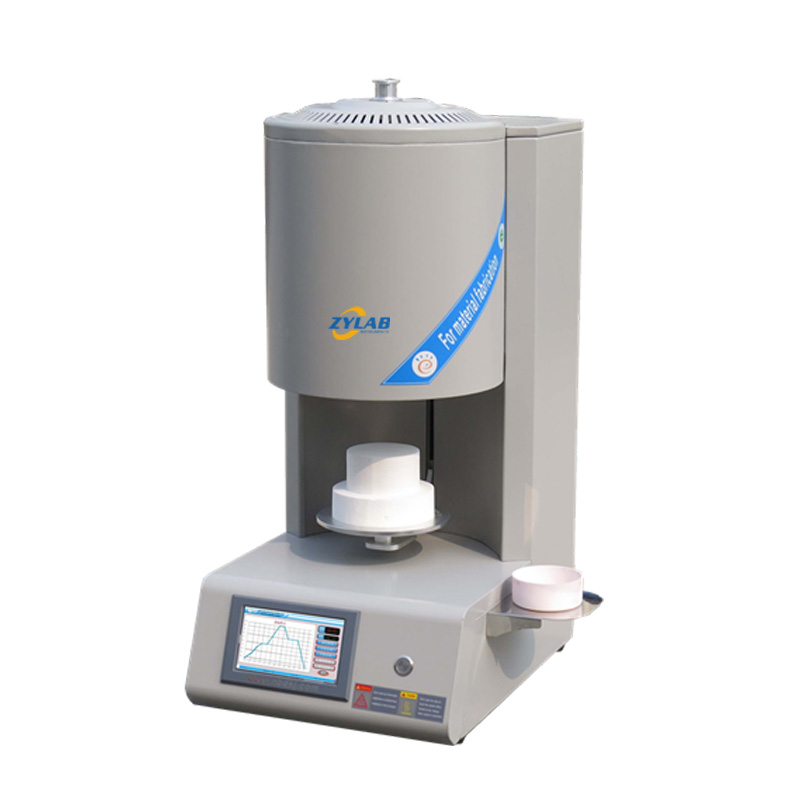
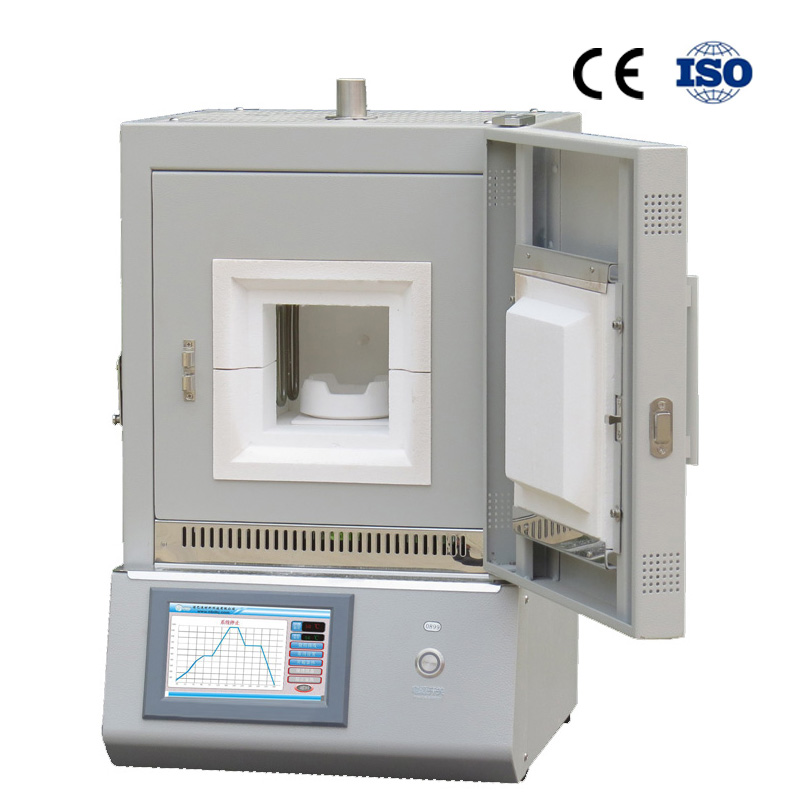
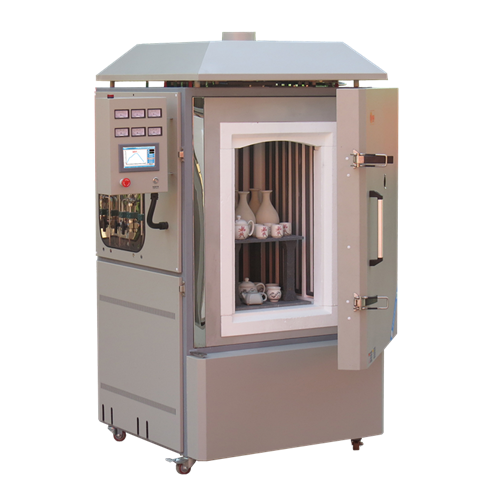
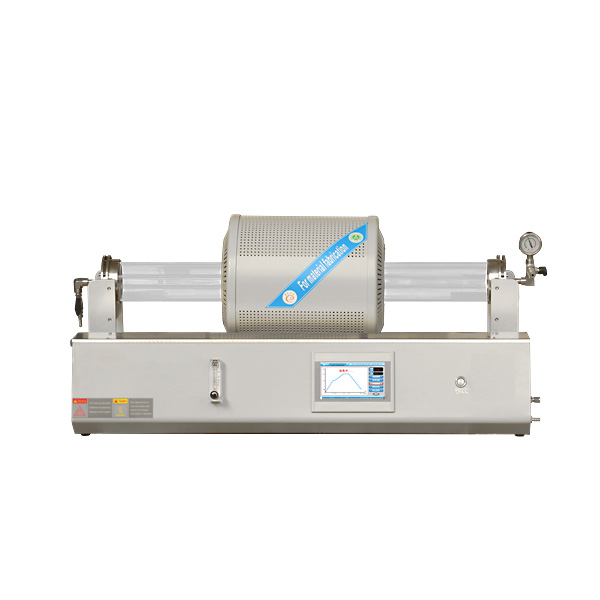
The Annealing Furnace Provided by ZYLAB
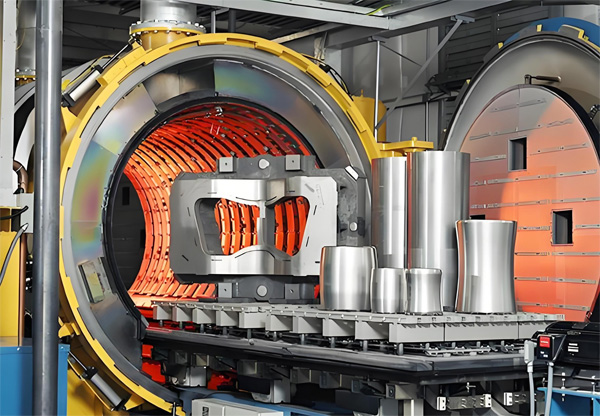
The Sintering Furnace Provided by ZYLAB
Operation Differences:
The operation of an annealing furnace is typically relatively simple. Operators only need to possess basic operational skills, understand the annealing conditions of the materials, then set the temperature and time parameters, and start the heating device to begin the annealing process.
In the annealing process, maintaining a constant temperature and appropriate annealing time is crucial. Therefore, operators need to closely monitor temperature changes and promptly adjust control parameters.
Operating a sintering furnace is more complex because the sintering process involves diffusion, solidification, and bonding between particles. It involves controlling multiple parameters such as temperature, atmosphere, pressure, and requires more operational steps and technical control.
Since operating a sintering furnace involves the physical and chemical properties of materials, operators need to have a deep understanding of material characteristics to conduct appropriate operations and adjustments based on the properties of different materials.
Application Differences
Different Processing Objects:
Annealing Furnace: Primarily used for annealing metals, glass, plastics, etc., to adjust the crystal structure of the material, relieve internal stress, and improve properties such as toughness and ductility.
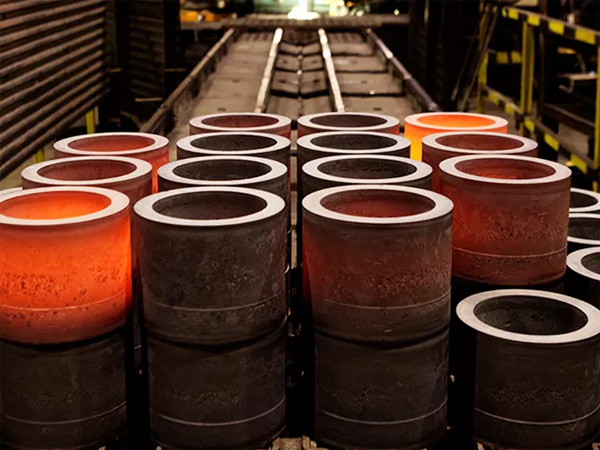
Sintering Furnace: Mainly used for sintering powder or granular metals, ceramics, etc., to form block-shaped objects, improving properties such as density and strength.
Different Process Objectives:
Annealing Furnace: Mainly used to improve the mechanical properties, processability, and corrosion resistance of materials to meet the requirements of different industrial fields.
Sintering Furnace: Mainly used to achieve specific process requirements in fields such as powder metallurgy, ceramic manufacturing, electronic materials, etc., such as preparing products with specific shapes, densities, and structures.
Different Process Conditions:
Annealing Furnace: The annealing process generally requires controlling parameters such as temperature, time, and cooling rate. It often takes place under atmospheric conditions, and sometimes requires inert atmosphere or atmosphere control conditions.
Sintering Furnace: The sintering process requires higher temperature and atmosphere control, typically carried out under inert atmosphere to prevent material oxidation. It also requires control of sintering rate and pressure parameters.
Different Application Fields:
Annealing Furnace: Widely used in fields such as metal processing, glass manufacturing, plastic molding, semiconductor manufacturing, etc.
Sintering Furnace: Mainly used in fields such as powder metallurgy, ceramic manufacturing, electronic materials, etc.