Table of Contents
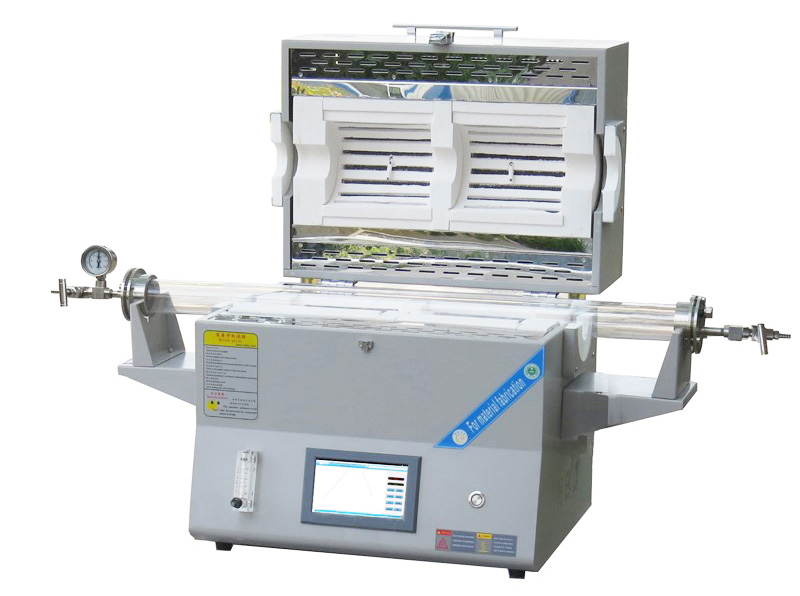
Images of Two Zone Tube Furnace
Overview
A two zone tube furnace is a type of high-temperature furnace with two independently controlled heating zones.
It consists of a cylindrical tube or chamber made of high-temperature-resistant materials, typically quartz or ceramic, and two separate heating elements that allow for precise temperature control in different sections of the furnace.
This design enables researchers and industrial users to create varying temperature profiles within a single furnace for specific material processing requirements.
Two zone tube furnace used in various industrial, research, and laboratory settings for processes like material synthesis, heat treatment, and more.
Features
1. Two independently controlled heating zones.
2. High-temperature resistance materials for the furnace tube.
3. Accurate temperature control and monitoring.
4. Programmable temperature profiles.
5. Gas or vacuum atmosphere control options.
6. Various tube sizes and configurations.
Work Process
A two-zone tube furnace operates through a well-controlled process to heat, anneal, or process materials. The two heating zones allow for precise temperature control and gradients along the length of the tube.
Here’s a step-by-step overview of the work process:
Preparation: Load the sample or material into a suitable container, often in the form of a tube, boat, or crucible.
Position the sample within the tube, ensuring even spacing within the heating zones.
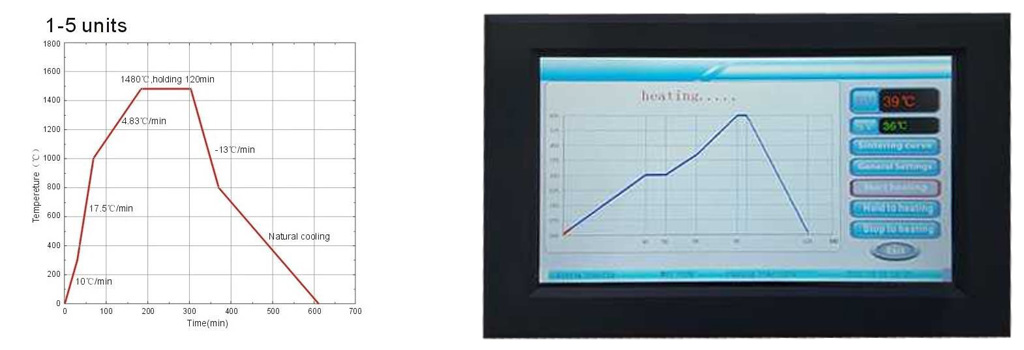
Setting Parameters: Specify the desired temperature profiles and set the heating zones independently. The temperature profiles are typically controlled using a digital control panel or computer interface.
Heating: Turn on the heating elements for each zone. These elements can be resistance wires, silicon carbide rods, or induction coils, depending on the furnace type.
The temperature gradually rises as the heating elements radiate heat onto the sample.
Temperature Control: Continuously monitor and control the temperature using built-in sensors and feedback mechanisms.
Achieve the desired temperature profile by adjusting the heating power and timing for each zone.
Processing: The sample undergoes the intended process such as crystallization, sublimation, chemical reactions, or annealing.
The ability to control temperature gradients allows for precise control over material properties.
Cooling:Once the process is completed, gradually cool the sample by reducing the heating power.
Some furnaces have rapid cooling options or use inert gases to control the cooling rate.
Sample Retrieval:Carefully remove the processed sample once it has cooled to a safe handling temperature.
Applications
Two-zone tube furnaces are versatile and find applications in a wide range of industries and research areas, including:
Materials Science: Crystal growth, thin-film deposition, and annealing.
Chemistry: Chemical vapor deposition, sublimation, and pyrolysis.
Nanotechnology: Synthesis of nanomaterials.
Electronics: Semiconductor manufacturing and device testing.
Ceramics: Sintering and glazing.
Metallurgy: Heat treatment and alloy development.
Benefits
1. Precise temperature control for complex material processing.
2. Uniform heating for improved material quality.
3. Versatility in creating customized temperature profiles.
4. Efficiency and scalability for research and industrial applications.
5. Safety features and protection against overheating.
Price
The price of a two-zone tube furnace can vary significantly depending on factors such as the size, temperature range, materials, and additional features. Entry-level models may start at a few thousand dollars, while more advanced and larger models can cost tens of thousands or more.
Considerations When Purchasing
Temperature Range: Ensure the furnace can reach the required temperature for your specific applications.
Tube Material: Consider the compatibility of the furnace tube material with your processes and sample materials.
Heating Element Type: Choose between resistance heating or induction heating based on your needs.
Control System: Look for user-friendly temperature control and data logging options.
Safety Features: Check for safety interlocks, over-temperature protection, and gas flow control.
Size and Configuration: Select a size that suits your sample size and desired temperature profile.
FAQ
1. Can I use a two-zone tube furnace for sintering materials?
Yes, these furnaces are often used for sintering processes, as they provide precise temperature control.
2. What is the maximum temperature a two-zone tube furnace can reach?
The maximum temperature depends on the model and design. It can range from a few hundred degrees Celsius to over 1700°C.
3. Can I program and save temperature profiles for later use?
Yes, many modern two-zone tube furnaces allow for programmable temperature profiles and data logging.
4. How do I clean the heating elements and furnace tube?
Cleaning methods vary based on the furnace design and materials used. Consult the manufacturer’s guidelines for cleaning and maintenance.
5. What type of gases can be used for creating controlled atmospheres?
Common gases used include nitrogen, argon for various process requirements.
6. Can I use a two-zone tube furnace in a vacuum environment?
Yes, most models can be adapted for vacuum operation.







